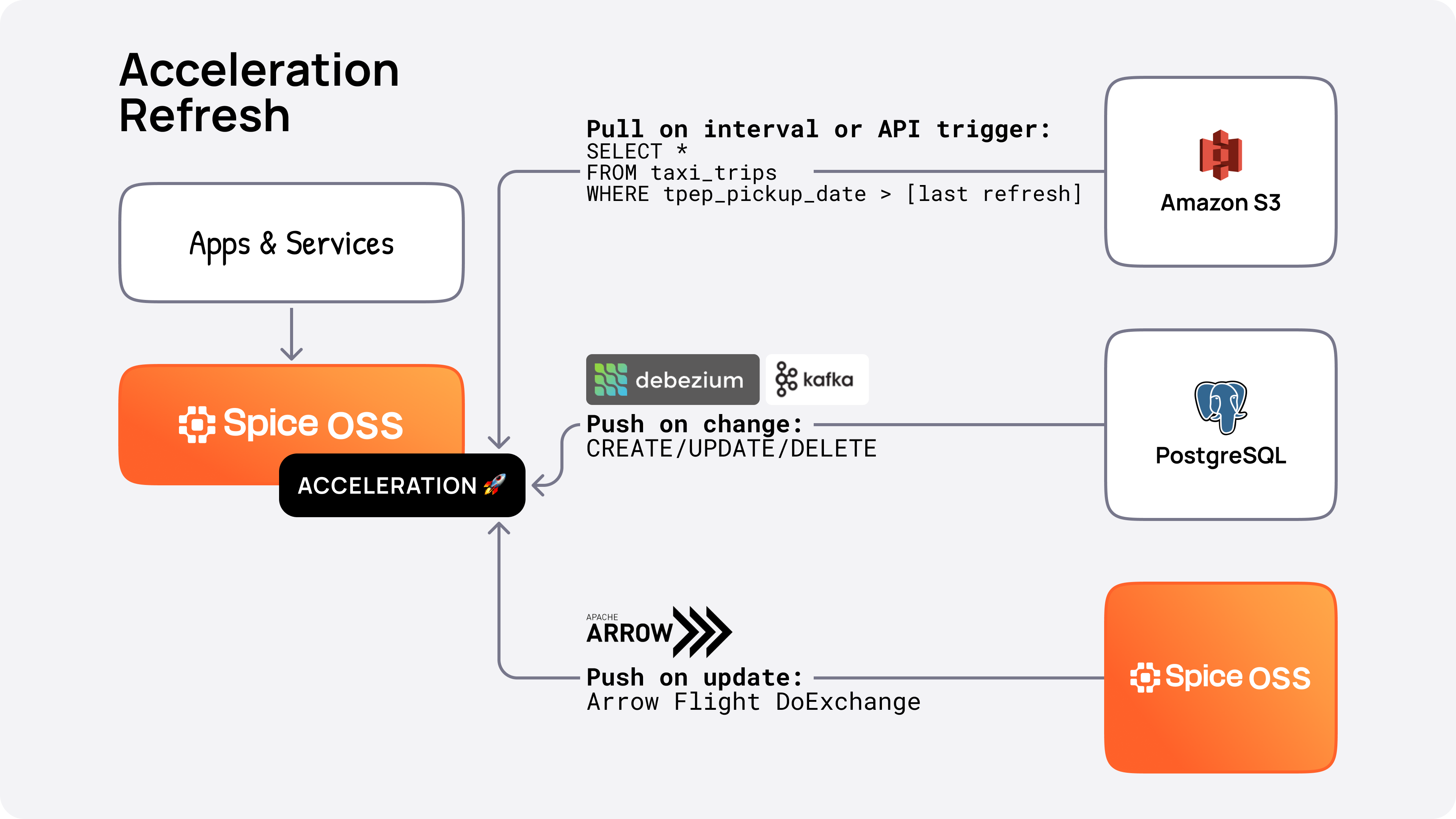
Data Refresh
Acceleration data can be refreshed (updated) by:
-
API: POST to
/v1/datasets/:name/acceleration/refresh. See Refresh Dataset HTTP API. -
Interval: Time-based refresh interval. See Refresh Interval.
-
Change Data Capture (CDC): CDC from a database using Debezium. See Change Data Capture.
-
Push: Spice-to-Spice Push over Apache Arrow DoExchange.
 .
.
Refresh Modes
Spice supports four modes to refresh/update local data from a connected data source. full is the default mode.
| Mode | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
full | Replace/overwrite the entire dataset on each refresh | A table of users |
append | Append/add data to the dataset on each refresh | Append-only, immutable datasets, such as time-series or log data |
changes | Apply incremental changes | Customer order lifecycle table |
caching | Read-through caching for SQL queries | API search results or dynamic content endpoints |
Learn more about each mode:
Example:
datasets:
- from: databricks:my_dataset
name: accelerated_dataset
acceleration:
refresh_mode: full
refresh_check_interval: 10m
Append
Using refresh_mode: append requires the use of a time_column dataset parameter, specifying a column to compare the local acceleration against the remote source. Data will be incrementally refreshed where the time_column value in the remote source is greater-than (gt) the max(time_column) value in the local acceleration.
E.g.
datasets:
- from: databricks:my_dataset
name: accelerated_dataset
time_column: created_at
acceleration:
refresh_mode: append
refresh_check_interval: 10m
Append-mode accelerations that define a time_column wait to report ready until the first append refresh completes after snapshot bootstrap. This keeps the dataset out of rotation until the freshest data is available while still benefiting from the snapshot-assisted startup.
If late arriving data or clock-skew needs to be accounted for, an optional overlap can also be specified. See acceleration.refresh_append_overlap.
time_partition_column
Datasets that are partitioned by a less-granular time-column (e.g. day, month, year) can also use the time_partition_column parameter in addition to the time_column parameter to specify the time-column to use for efficient partition pruning.
Example:
datasets:
- from: databricks:my_dataset
name: accelerated_dataset
time_column: created_at
time_format: iso8601
time_partition_column: created_at_day
time_partition_format: date
Append only modified files
Spice can automatically detect and append only newly created or updated files from object-store data sources. This is useful for append-only datasets where only new files are added to the source and existing files are not modified or deleted.
Enable this feature by setting either time_column or time_partition_column to the special value last_modified. When configured this way with refresh_mode: append, Spice will use the file/object's metadata to determine which files are new or have been updated.
This approach can drastically speed up incremental updates for large datasets, as Spice only needs to process the new files rather than scanning the entire dataset for changes to a column. This optimization is particularly valuable for datasets with many files or large file sizes.
If last_modified already exists as a column in the parquet data, that column will take precedence over the metadata value from the file itself.
Example using time_column:
datasets:
- from: s3://my_bucket/my_dataset
name: accelerated_dataset
time_column: last_modified
params:
file_format: parquet
acceleration:
refresh_mode: append
refresh_check_interval: 10m
Example using time_partition_column:
datasets:
- from: s3://my_bucket/my_dataset
name: accelerated_dataset
time_column: created_at
time_partition_column: last_modified
params:
file_format: parquet
acceleration:
refresh_mode: append
refresh_check_interval: 10m
Appending modified files is only supported for datasets that support setting the file format parameter, such as s3://, abfs://, file://, etc.
Changes (CDC)
Datasets configured with acceleration refresh_mode: changes requires a Change Data Capture (CDC) supported data connector. Initial CDC support in Spice is supported by the Debezium data connector.
Caching
The caching refresh mode is designed for HTTP-based datasets where request metadata acts as cache keys. This mode is particularly useful for API responses that return multiple rows for a single request, such as search results or dynamic content endpoints.
See Caching Mode for detailed documentation and examples.
Ready State
Supported in refresh_mode | Any |
| Required | No |
| Default Value | on_load |
By default, Spice will return an error for queries against an accelerated dataset that is still loading its initial data. The endpoint /v1/ready is used in production deployments to control when queries are sent to the Spice runtime.
The ready state for an accelerated dataset can be configured using the ready_state parameter in the dataset configuration.
ready_state: on_load: Default. The dataset is considered ready after the initial load of the accelerated data. For file-based accelerated datasets that have existing data, this will be ready immediately. Queries against this dataset before the data is loaded will return an error.ready_state: on_registration: The dataset is considered ready when the dataset is registered in Spice, even before the initial data is loaded. Queries against this dataset before the data is loaded will automatically fallback to the federated source. Once the data is loaded, queries will be served from the acceleration.
Example:
datasets:
- from: s3://my_bucket/my_dataset
name: my_dataset
ready_state: on_load # or on_registration
acceleration:
enabled: true
Fast Cold Starts with Snapshots
File-based acceleration engines (DuckDB or SQLite) can rely on acceleration snapshots to download a pre-built database file on startup instead of waiting for the first refresh to finish. Configure a shared snapshot location under the top-level snapshots block and opt individual datasets in with acceleration.snapshots: enabled, bootstrap_only, or create_only. Snapshots are stored using Hive-style partitions (month=YYYY-MM/day=YYYY-MM-DD/dataset=<name>) and are only supported when each dataset writes to its own acceleration file.
Filtered Refresh
Typically only a working subset of an entire dataset is used in an application or dashboard. Use these features to filter refresh data, creating a smaller subset for faster processing and to reduce the data transferred and stored locally.
- Refresh SQL - Specify the filter as arbitrary SQL to be pushed down to the remote source.
- Refresh Data Window - Filters data from the remote source outside the specified time window.
Refresh SQL
Supported in refresh_mode | Any |
| Required | No |
| Default Value | Unset |
Refresh SQL supports specifying filters for data accelerated from the connected source using arbitrary SQL.
Filters will be pushed down to the remote source when possible, so only the requested data will be transferred over the network.
Example:
datasets:
- from: databricks:my_dataset
name: accelerated_dataset
acceleration:
enabled: true
refresh_mode: full
refresh_check_interval: 10m
refresh_sql: |
SELECT * FROM accelerated_dataset WHERE city = 'Seattle'
The refresh_sql parameter can be updated at runtime on-demand using PATCH /v1/datasets/:name/acceleration. This change is temporary and will revert to the spicepod.yml definition at the next runtime restart.
Columns can be selected in the query via the SELECT clause, but only column names are supported. Arbitrary expressions or aliases are not supported.
Example:
curl -i -X PATCH \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{
"refresh_sql": "SELECT city, state FROM accelerated_dataset WHERE city = 'Bellevue'"
}' \
127.0.0.1:8090/v1/datasets/accelerated_dataset/acceleration
Queries that return zero results will fallback to the behavior specified by the on_zero_results parameter, and will not have the refresh_sql applied to the results from the fallback. The refresh_sql only applies to acceleration refresh tasks.
For the complete reference, view the refresh_sql section of datasets.
- When
refresh_mode: changesis specified, Refresh SQL can only modify the selected columns and cannot apply filters. - Running queries while using refresh SQL will not fallback to the source if any query returns more than zero rows, even when querying against columns that are not explicitly filtered by the refresh SQL. This may result in queries returning partial data, depending on the filters applied in the refresh SQL.
- Refresh SQL only supports filtering data from the current dataset - joining across other datasets is not supported.
- Refresh SQL modifications made via API are temporary and will revert after a runtime restart.
Refresh Data Window
Supported in refresh_mode | full, append |
| Required | No |
| Default Value | Unset |
The refresh_data_window parameter supports refreshing data that falls within the specified time window. The refresh_data_window is applied cumulatively to any filters specified by the refresh_sql, and applies a time filter based on now() - refresh_data_window. For example, the following configuration:
time_column: column_time
acceleration:
refresh_sql: "SELECT * FROM my_dataset WHERE column_one = 'value'"
refresh_data_window: 1d
In this example, refresh_data_window is converted into an effective Refresh SQL of SELECT * FROM my_dataset WHERE column_one = 'value' AND column_time > (now() - interval '1' day). The time_column column can be specified in the refresh_sql in conjunction with the refresh_data_window, and both filters are combined with AND.
This parameter relies on the time_column dataset parameter specifying a column that is a timestamp type. Optionally, the time_format can be specified to instruct the Spice runtime on how to interpret timestamps in the time_column.
Example with refresh_sql:
datasets:
- from: databricks:my_dataset
name: accelerated_dataset
time_column: created_at
acceleration:
enabled: true
refresh_mode: full
refresh_check_interval: 10m
refresh_sql: |
SELECT * FROM accelerated_dataset WHERE city = 'Seattle'
refresh_data_window: 1d
This example will only accelerate data from the federated source that matches the filter city = 'Seattle' and is less than 1 day old.
Example with on_zero_results:
datasets:
- from: databricks:my_dataset
name: accelerated_dataset
time_column: created_at
acceleration:
enabled: true
refresh_mode: full
refresh_check_interval: 10m
refresh_sql: |
SELECT * FROM accelerated_dataset WHERE city = 'Seattle'
refresh_data_window: 1d
on_zero_results: use_source
This example will only accelerate data from the federated source that matches the filter city = 'Seattle' and is less than 1 day old. If a query against the accelerated data returns zero results, the query will fallback to the source and return the direct results without any filtering.
If a query against the accelerated data returns some results, the query will not fall back. For example, attempting to query for the last 2 days of data would only return the last 1 day of data without falling back.
Behavior on Zero Results
Supported in refresh_mode | full, append |
| Required | No |
| Default Value | return_empty |
By default, accelerated datasets only return locally materialized data. If this local data is a subset of the full dataset in the federated source—due to settings like refresh_sql, refresh_data_window, or retention policies—queries against the accelerated dataset may return zero results, even when the federated table would return results.
To address this, on_zero_results: use_source can be configured in the acceleration configuration. Queries returning zero results will fall back to the federated source, returning results from querying the underlying data.
on_zero_results:
return_empty(Default) - Return an empty result set when no data is found in the accelerated dataset.use_source- Fall back to querying the federated table when no data is found in the accelerated dataset.
Example:
datasets:
- from: databricks:my_dataset
name: accelerated_dataset
acceleration:
enabled: true
refresh_sql: SELECT * FROM accelerated_dataset where city = 'Seattle'
on_zero_results: use_source
In this example a query against accelerated_dataset within Spice like SELECT * FROM accelerated_dataset WHERE city = 'Portland' would initially query against the accelerated data, see that it returns zero results and then fallback to querying against the federated table in Databricks.
- It is possible that even though an accelerated table returns some results, it may not contain all the data that would be returned by the federated table.
on_zero_resultsonly controls the behavior in the simple case where no data is returned by the acceleration for a given query.
Refresh on Startup
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
Supported in refresh_mode | Any |
| Required | No |
| Default Value | auto |
Controls the refresh behavior of an accelerated dataset across restarts.
refresh_on_startup Options:
auto(Default) – Maintains refresh state across restarts:- With
refresh_check_interval: Schedules next refresh based on last successful refresh time, triggering immediately if interval has already elapsed - Without
refresh_check_interval: No refresh (on-demand only)
- With
always– Forces a dataset refresh on every startup, regardless of the existing acceleration state.
Setting refresh_on_startup: always ensures that accelerated data is always refreshed to match the source when the service restarts. This is useful in development environments or when data consistency is critical after deployment.
Example Configuration:
datasets:
- from: databricks:my_dataset
name: accelerated_dataset
acceleration:
enabled: true
refresh_on_startup: always
For the complete reference, view the refresh_on_startup section of datasets.
Refresh Interval
Supported in refresh_mode | full, append |
| Required | No |
| Default Value | Unset |
The refresh_check_interval parameter controls how often the accelerated dataset is refreshed.
Example:
datasets:
- from: spice.ai/spiceai/quickstart/datasets/taxi_trips
name: taxi_trips
acceleration:
enabled: true
refresh_mode: full
refresh_check_interval: 10s
This configuration will refresh taxi_trips data every 10 seconds.
Refresh On-Demand
Supported for accelerators with a refresh_mode of full or append.
Accelerated datasets can be refreshed on-demand via the refresh CLI command or POST /v1/datasets/:name/acceleration/refresh API endpoint.
CLI example:
spice refresh eth_recent_blocks
API example using cURL:
curl -i -XPOST 127.0.0.1:8090/v1/datasets/eth_recent_blocks/acceleration/refresh
with response:
HTTP/1.1 201 Created
content-type: application/json
content-length: 55
date: Thu, 11 Apr 2024 20:11:18 GMT
{"message":"Dataset refresh triggered for eth_recent_blocks."}
On-demand refresh always initiates a new refresh, terminating any in-progress refresh for the dataset.
Refresh Schedules
Supported in refresh_mode | full, append |
| Required | No |
| Default Value | Unset |
The refresh_cron parameter supports specifying a cron schedule which controls when datasets refresh.
Example:
datasets:
- from: spice.ai/spiceai/quickstart/datasets/taxi_trips
name: taxi_trips
acceleration:
enabled: true
refresh_mode: full
refresh_cron: '0 12 * * 1-5'
This configuration will refresh taxi_trips data at midday every weekday. For more information about cron schedules, see the cron schedule reference.
The refresh_cron parameter cannot be specified in conjunction with a refresh_check_interval parameter.
Refresh Retries
Supported in refresh_mode | full, append |
| Required | No |
Default refresh_retry_enabled | false |
Default refresh_retry_max_attempts | Unset |
By default, data refreshes for accelerated datasets are retried on transient errors (connectivity issues, compute warehouse goes idle, etc.) using a Fibonacci backoff strategy.
Retry behavior can be configured using the acceleration.refresh_retry_enabled and acceleration.refresh_retry_max_attempts parameters.
Example: Disable retries
datasets:
- from: spice.ai/spiceai/quickstart/datasets/taxi_trips
name: taxi_trips
acceleration:
refresh_retry_enabled: false
refresh_check_interval: 30s
Example: Limit retries to a maximum of 10 attempts
datasets:
- from: spice.ai/spiceai/quickstart/datasets/taxi_trips
name: taxi_trips
acceleration:
refresh_retry_max_attempts: 10
refresh_check_interval: 30s
Retention Policy
Supported in refresh_mode | full, append |
| Required | No |
Default retention_check_enabled | false |
Default retention_period | Unset |
Default retention_sql | Unset |
Default retention_check_interval | Unset |
Accelerated datasets can be configured to automatically evict data using two different retention strategies:
Time-based Retention
Automatically evict time-series data exceeding a retention period by setting a retention policy based on the configured time_column and acceleration.retention_period.
The policy is set using the acceleration.retention_check_enabled, acceleration.retention_period and acceleration.retention_check_interval parameters, along with the time_column and time_format dataset parameters.
When retention_check_enabled is set to true, retention_check_interval and retention_period are required parameters.
Example:
datasets:
- from: mysql:user_events
name: user_events
time_column: created_at
acceleration:
enabled: true
refresh_mode: append
retention_check_enabled: true
retention_period: 30d
retention_check_interval: 1h
Custom SQL-based Retention
Evict data from an acceleration based on custom filter predicates using the acceleration.retention_sql parameter. This is useful for scenarios like soft-deleting rows in append datasets or removing data based on complex business logic.
The retention_sql parameter takes the form of a DELETE FROM <table> WHERE <predicates> statement.
Example - Soft delete retention:
datasets:
- from: mysql:user_events
name: user_events
time_column: created_at
acceleration:
enabled: true
refresh_mode: append
primary_key: user_id
on_conflict:
user_id: upsert
retention_check_enabled: true
retention_check_interval: 5m
retention_sql: DELETE FROM user_events WHERE status = 'archived'
- Time-based retention (
retention_period) and custom SQL retention (retention_sql) can be used independently or together. When both are configured, both retention policies will be applied during each retention check.
Refresh Jitter
Supported in refresh_mode | full, append |
| Required | No |
Default refresh_jitter_enabled | false |
Default refresh_jitter_max | Unset |
Accelerated datasets can include a random jitter in their refresh interval to prevent the Thundering herd problem, where multiple datasets refresh simultaneously. The jitter is a random value between 0 and refresh_jitter_max, which is added to or subtracted from the base refresh_check_interval. If refresh_jitter_max is not specified, it defaults to 10% of refresh_check_interval.
Refresh Jitter applies to the initial dataset load. If multiple similarly configured Spice instances are restarted at the same time, they will load with a jitter between 0 and refresh_jitter_max.
Example:
datasets:
- from: spice.ai/spiceai/quickstart/datasets/taxi_trips
name: taxi_trips
acceleration:
refresh_check_interval: 10s
refresh_jitter_enabled: true
refresh_jitter_max: 1s
In the configuration above:
- The initial load will include a random delay between 0 and 1 second.
- Subsequent refresh intervals will vary randomly between 9 seconds and 11 seconds.
Refresh jitter configuration:
Configuration Examples
Accelerating a full set of data that sometimes changes
In this example, Spice connects with a dataset that changes infrequently and is not configured for CDC. For example, a list of product categories.
datasets:
- from: mysql:product_categories
name: product_categories
acceleration:
refresh_mode: full
refresh_check_interval: 8h
In this scenario, Spice uses a simple acceleration configuration - full refreshes on an 8 hour schedule. No additional behaviors are enabled, so queries matching for new product codes will return no results until the next refresh cycle.
Accelerating a subset of data that changes frequently
In this example, Spice connects with a dataset that has frequently changing data that is not configured for CDC. For example, user's posts on a social media platform.
datasets:
- from: mysql:posts
name: posts
acceleration:
refresh_mode: full
refresh_check_interval: 10m
refresh_sql: "SELECT * FROM posts WHERE updated_at > now() - interval '1' day"
on_zero_results: use_source
With this configuration, Spice will refresh every 10 minutes accelerating posts that have been updated in the last day.
When querying for posts by direct ID, if a post is not accelerated Spice will fallback to retrieving the post from the non-accelerated source due to the behavior of on_zero_results: use_source.
However, if querying for a range of posts that includes some which have updated in the last day Spice will only return those results without falling back to the source. This could result in queries for a range of posts excluding posts that exist in the non-accelerated source because they have been filtered out due to their updated_at value.
Accelerating application logs
In this example, Spice connects to a data source that is immutable, receives new rows, and is not configured for CDC. For example, a database that contains some application logs.
datasets:
- from: duckdb:logs
name: logs
time_column: created_at
params:
duckdb_open: logs.duckdb
acceleration:
refresh_mode: append
refresh_check_interval: 10m
refresh_sql: "SELECT * FROM logs WHERE asset = 'asset_id'"
refresh_data_window: 1d
on_zero_results: use_source
retention_check_enabled: true
retention_period: 7d
retention_check_interval: 10m
This acceleration configuration applies a number of different behaviors:
- A
refresh_data_windowwas specified. When Spice starts, it will apply thisrefresh_data_windowto therefresh_sql, and retrieve only the last day's worth of logs with anasset = 'asset_id'. - Because a
refresh_sqlis specified, every refresh (including initial load) will have the filter applied to the refresh query. - 10 minutes after loading, as specified by the
refresh_check_interval, the first refresh will occur - retrieving new rows whereasset = 'asset_id'. - Running a query to retrieve logs with an
assetthat is notasset_idwill fall back to the source, because of theon_zero_results: use_sourceparameter. - Running a query to retrieve a log longer than 1 day ago will fall back to the source, because of the
on_zero_results: use_sourceparameter. - Running a query to retrieve logs within a range of now to longer than 1 day ago will only return logs from the last day. This is due to the
refresh_data_windowonly accelerating the last day's worth of logs, which will return some results. Because results are returned, Spice will not fall back to the source even thoughon_zero_results: use_sourceis specified. - Spice will retain newly appended log rows for 7 days before discarding them, as specified by the
retention_*parameters.
Cookbook
- Configure accelerated dataset retention policy. Accelerated Dataset Retention Policy
- Dynamically refresh specific data at runtime by programmatically updating refresh_sql and triggering data refreshes. Advanced Data Refresh
- Configure
refresh_data_windowto filter refreshed data to recent data Refresh Data Window
