Spice Cayenne Data Accelerator
The Spice Cayenne Data Accelerator is in Beta.
Spice Cayenne is a data acceleration engine designed for high-performance, scalable query on large-scale datasets. Built on Vortex, a high-performance columnar file format, Spice Cayenne combines columnar storage with in-process metadata management to provide fast query performance to scale to datasets beyond 1TB.
Why Vortex?
Spice Cayenne uses Vortex as its storage format, providing significant performance advantages:
- 100x faster random access reads compared to modern Apache Parquet
- 10-20x faster scans for analytical queries
- 5x faster writes with similar compression ratios
- Zero-copy compatibility with Apache Arrow for efficient data processing
- Extensible architecture with pluggable encoding, compression, and layout strategies
Vortex is a Linux Foundation (LF AI & Data) project under Apache-2.0 license with neutral governance. For performance benchmarks, see bench.vortex.dev.
While DuckDB excels for datasets up to approximately 1TB, Spice Cayenne with Vortex is designed to scale beyond these limits.
Architecture
Spice Cayenne follows a lakehouse architecture inspired by DuckLake, separating metadata management from data storage:
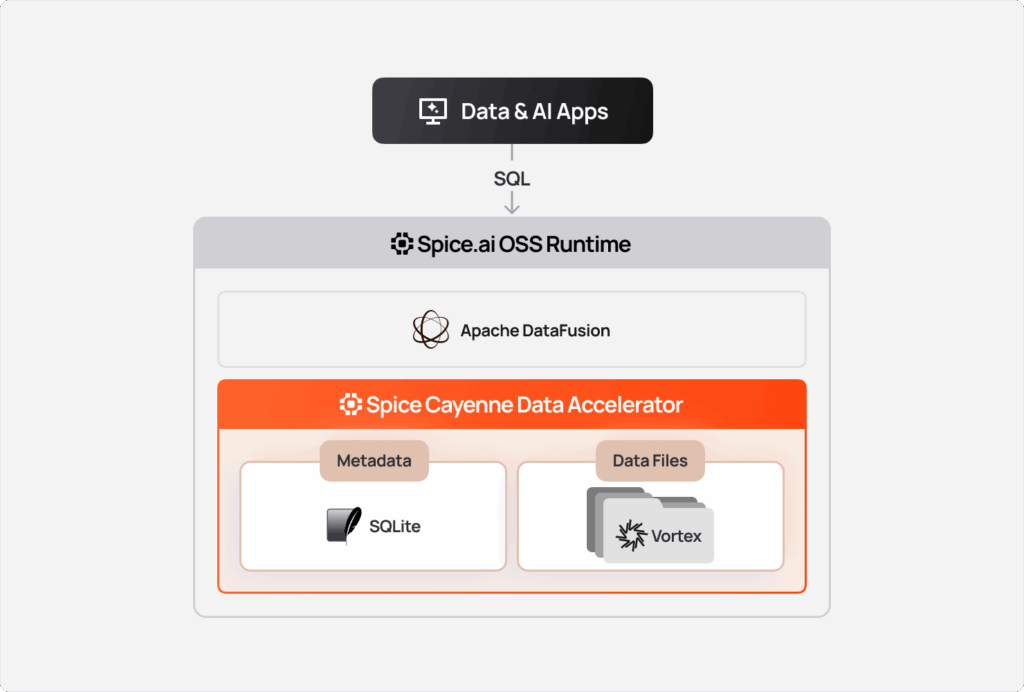
Key Design Principles:
- Virtual Files: Each "file" is a Vortex
ListingTableat a unique directory, enabling append operations and parallel reads - Lazy Statistics: Summary statistics are loaded on-demand for query optimization
- Sequence-based Ordering: Iceberg-style sequence numbers enable upsert semantics without requiring separate tracking of "undeleted" records (rows that were deleted and then re-inserted)
- Pluggable Storage: Data files can be stored locally or in S3 Express One Zone while metadata remains local
Storage Recommendations
For optimal performance, store Cayenne data files on NVMe storage. NVMe provides the lowest latency and highest throughput for the random access patterns that Vortex files require.
Use S3 Express One Zone when persistence of accelerations across restarts is required. S3 Express One Zone adds network latency compared to local NVMe but provides durability. Sharing accelerated data across multiple Spice instances is planned for a future release.
Configuration
To use Spice Cayenne as the data accelerator, specify cayenne as the engine for acceleration. Spice Cayenne only supports mode: file and stores data on disk.
datasets:
- from: spice.ai:path.to.my_dataset
name: my_dataset
acceleration:
engine: cayenne
mode: file
params
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
cayenne_compression_strategy | Compression algorithm for accelerated data. Defaults to btrblocks. Supports btrblocks or zstd. |
cayenne_unsupported_type_action | Action when an unsupported data type is encountered. See Data Type Support. |
cayenne_footer_cache_mb | Size of the in-memory Vortex footer cache in megabytes. Larger values improve query performance for repeated scans. Defaults to 128. |
cayenne_segment_cache_mb | Size of the in-memory Vortex segment cache in megabytes, caching decompressed data segments for improved query performance. Defaults to 256. |
cayenne_file_path | Custom path for storing Cayenne data files. Supports local paths or S3 Express One Zone URLs (e.g., s3://bucket--usw2-az1--x-s3/prefix/). |
cayenne_target_file_size_mb | Target size for individual Vortex files in MB. When writes exceed this size, a new Vortex file is created. Defaults to 128. Smaller files enable better parallelism and predicate pushdown. |
cayenne_metadata_dir | Custom directory for storing Cayenne metadata (SQLite catalog). Defaults to {spice_data_path}/metadata. |
cayenne_metastore | Metastore backend type. Supports sqlite (default) or turso (requires turso feature flag). |
sort_columns | Comma-separated list of columns to sort data by on refresh operations. Improves segment pruning for frequently filtered columns. |
unsupported_type_action | Action when encountering unsupported data types. Options: error (default), warn, ignore, string. |
S3 Express One Zone Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
cayenne_s3_zone_ids | Comma-separated availability zone IDs (e.g., usw2-az1,usw2-az2). Auto-generates bucket names in format spice-{app}-{dataset}--{zone}--x-s3. |
cayenne_s3_region | AWS region (e.g., us-west-2). Auto-derived from zone ID if not specified. |
cayenne_s3_auth | Authentication method: iam_role (default) or key. |
cayenne_s3_key | AWS access key ID (required when cayenne_s3_auth: key). |
cayenne_s3_secret | AWS secret access key (required when cayenne_s3_auth: key). |
cayenne_s3_session_token | AWS session token (optional, for temporary credentials). |
cayenne_s3_endpoint | Custom S3 endpoint URL (optional, overrides auto-generated endpoint). |
cayenne_s3_client_timeout | Request timeout duration (e.g., 5m). Defaults to 5 minutes for uploads. |
cayenne_s3_allow_http | Set to true for testing with local S3-compatible storage. Defaults to false. |
Performance Tuning
Spice Cayenne performance can be optimized through cache configuration, compression strategy selection, and resource allocation.
Cache Tuning
Spice Cayenne uses two in-memory caches to accelerate query performance:
Footer Cache (cayenne_footer_cache_mb):
The footer cache stores Vortex file metadata, including schemas, statistics, and encoding information. Larger cache sizes benefit workloads with many files.
- Default: 128 MB
- Increase for datasets with many small files
- Each file requires approximately 1-10 KB of footer cache
Segment Cache (cayenne_segment_cache_mb):
The segment cache stores decompressed data segments. Larger cache sizes benefit workloads with repeated queries on the same data.
- Default: 256 MB
- Increase for workloads with hot data patterns
- Size based on frequently accessed data volume
Example - High-throughput configuration:
datasets:
- from: s3://analytics-bucket/events/
name: events
acceleration:
engine: cayenne
mode: file
params:
cayenne_footer_cache_mb: 512
cayenne_segment_cache_mb: 1024
Compression Strategy
Spice Cayenne supports two compression strategies, each with different performance characteristics. The BtrBlocks compression algorithm is designed for fast analytical queries, while zstd provides fast write performance. Additionally, zstd achieves better compression ratios when data contains large chunks of binary or text.
| Strategy | Compression | Read Speed | Write Speed | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|---|
btrblocks | Higher | Faster | Moderate | Read-heavy analytics (default) |
zstd | High | Moderate | Faster | Write-heavy workloads, large binary or text data |
Example - Write-optimized configuration:
datasets:
- from: kafka:events
name: realtime_events
acceleration:
engine: cayenne
mode: file
refresh_mode: append
params:
cayenne_compression_strategy: zstd
File Size Tuning
The cayenne_target_file_size_mb parameter controls when new Vortex files are created during writes:
- Smaller files (32-64 MB): Better parallelism, finer-grained statistics, faster ingestion
- Larger files (128-256 MB): Fewer files to manage, reduced metadata overhead
params:
cayenne_target_file_size_mb: 64 # More parallelism for high-concurrency workloads
Features
DataFusion Query-Native Execution
Spice Cayenne is DataFusion query-native, meaning all query execution uses Apache DataFusion and adheres to the runtime.query.memory_limit setting. This provides:
- Vectorized execution: Multi-threaded, SIMD-optimized query processing
- Automatic memory management: Query memory is tracked and spilled to disk when limits are exceeded
- Dynamic filter pushdown: Filters from TopK, Join, and Aggregate operators push down to file scans
DataFusion's FairSpillPool divides memory evenly among partitions, providing predictable memory usage under concurrent query load.
High-Performance Columnar Storage
Spice Cayenne uses Vortex's advanced columnar format, which provides:
- Efficient Compression: Cascading compression with nested encoding schemes including RLE, dictionary encoding, FastLanes, FSST, and ALP
- Rich Statistics: Lazy-loaded summary statistics for query optimization
- Extensible Encodings: Pluggable physical layouts optimized for different data patterns
- Wide Table Support: Efficient handling of tables with many columns through zero-copy metadata access
Point Lookups and Random Access
Vortex delivers 100x faster random access reads compared to Apache Parquet through several architectural features:
Segment Statistics (Zone-Map Equivalent):
Vortex's ChunkedLayout maintains per-segment statistics for each column, enabling segment pruning during query execution. Statistics include:
| Statistic | Description | Use Case |
|---|---|---|
min | Minimum value in segment | Range predicate pruning |
max | Maximum value in segment | Range predicate pruning |
null_count | Count of null values | IS NULL/IS NOT NULL optimization |
is_sorted | Whether segment is sorted | Binary search for point lookups |
is_constant | Whether all values are identical | Immediate value return |
When a query includes a WHERE clause, Spice Cayenne evaluates whether each segment could contain matching rows. Segments that cannot match based on min/max statistics are skipped entirely, similar to DuckDB's zone-maps without requiring explicit index creation.
Example - Segment Pruning:
For a table with segments containing timestamp ranges [2024-01-01, 2024-01-15], [2024-01-16, 2024-01-31], [2024-02-01, 2024-02-15], a query:
SELECT * FROM events WHERE timestamp > '2024-01-20'
Prunes the first segment (max < 2024-01-20) and reads only the second and third segments.
Fast Random Access Encodings:
Vortex encodings support direct random access to compressed data:
- FSST (Fast Static Symbol Table): String compression with O(1) random access
- FastLanes: High-performance integer encoding with vectorized decoding
- ALP: Adaptive lossless floating-point compression with random access
Compute Push-Down:
Vortex supports executing filter and compute operations directly on compressed data, avoiding full decompression for predicate evaluation. This compute push-down reduces CPU and memory overhead by processing data in its compressed form:
| Encoding | Data Type | Operations |
|---|---|---|
| FSST | Strings | Equality, prefix matching on compressed symbols |
| FastLanes | Integers | SIMD-accelerated comparison on bit-packed data |
| ALP | Floats | Range comparisons with minimal decompression |
| Dictionary | Any | Lookup predicates evaluated on dictionary indices |
| RLE | Any | Constant runs evaluated once per run |
Array-level statistics (is_sorted, is_constant, min, max) enable additional optimizations beyond filtering. For example, is_sorted enables binary search for point lookups, and is_constant returns values immediately without scanning.
Performance Characteristics:
For point lookups and selective queries, Spice Cayenne with Vortex often matches or exceeds the performance of traditional B-tree indexes while consuming no additional memory for index structures. Performance scales with:
- Data sorting (sorted columns benefit most from segment pruning)
- Segment cache hit rate (hot data patterns)
- Compression encoding match to data characteristics
Deletion Vectors
Spice Cayenne implements efficient deletes without rewriting data files using deletion vectors. Deletion vectors track which rows have been logically deleted, and the information is applied transparently during query execution.
Deletion Strategies
Cayenne supports two deletion vector strategies based on your table configuration:
| Strategy | Use Case | Configuration | Memory per Delete |
|---|---|---|---|
| Position-based | Tables without primary key | No primary_key set | ~4 bytes (RoaringBitmap) |
| Key-based | Tables with primary key | primary_key configured | 8+ bytes per key |
Position-based deletion uses row position within the table. Cayenne uses RoaringBitmap for memory-efficient storage of deleted row IDs, providing 50-90% memory savings compared to HashSet for sparse deletions.
Key-based deletion uses the byte representation of primary key columns. This approach is position-independent and survives data reorganization, making it more reliable for tables with primary keys.
Primary Key Optimization
For tables with a single-column Int64 primary key, Cayenne uses an optimized direct lookup strategy that avoids serialization overhead:
datasets:
- from: s3://bucket/events/
name: events
acceleration:
engine: cayenne
mode: file
primary_key: event_id # Int64 column - uses optimized deletion
Upsert Support
When on_conflict is configured, Cayenne supports upsert semantics using sequence numbers (Iceberg-style ordering):
datasets:
- from: kafka:events
name: events
acceleration:
engine: cayenne
mode: file
primary_key: id
on_conflict:
id: upsert
When a primary key is deleted and then re-inserted:
- The new insert gets a higher sequence number than the delete
- During scan, the delete doesn't apply to data with higher sequence numbers
- The new data is visible without requiring separate tracking of "undeleted" records
AWS S3 Express One Zone Storage
Spice Cayenne supports storing data files in AWS S3 Express One Zone for single-digit millisecond latency, ideal for latency-sensitive query workloads that require persistence. Metadata remains on local disk for fast catalog operations while data files are stored in S3 Express One Zone.
Why S3 Express One Zone?
S3 Express One Zone directory buckets provide:
- Single-digit millisecond latency: 10x faster than S3 Standard for first-byte latency
- High request throughput: Up to 10x higher request rates than S3 Standard
- Cost efficiency: Lower per-request costs for high-frequency access patterns
- Durability: Same 99.999999999% (11 9s) durability as S3 Standard
S3 Express Examples
Example 1 - Explicit bucket:
datasets:
- from: s3://source-bucket/events/
name: analytics_events
acceleration:
engine: cayenne
enabled: true
mode: file
params:
# Store data in S3 Express One Zone bucket
cayenne_file_path: s3://my-bucket--usw2-az1--x-s3/cayenne/
cayenne_s3_region: us-west-2
Example 2 - Auto-generated bucket with IAM role:
datasets:
- from: postgresql://db/events
name: fast_events
acceleration:
engine: cayenne
enabled: true
mode: file
params:
# Auto-generates bucket: spice-{spicepod-name}-fast_events--usw2-az1--x-s3
cayenne_s3_zone_ids: usw2-az1
Example 3 - Explicit credentials:
datasets:
- from: kafka:events
name: realtime
acceleration:
engine: cayenne
enabled: true
mode: file
params:
cayenne_s3_zone_ids: use1-az4
cayenne_s3_region: us-east-1
cayenne_s3_auth: key
cayenne_s3_key: ${secrets:AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID}
cayenne_s3_secret: ${secrets:AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY}
Bucket Naming Conventions
S3 Express One Zone buckets use a specific naming format:
- Format:
{base-name}--{zone-id}--x-s3 - Zone ID format:
{region-code}-az{number}(e.g.,usw2-az1,use1-az4) - Auto-generated names:
spice-{app-name}-{dataset-name}--{zone-id}--x-s3
The zone ID is automatically extracted from the bucket name to configure the correct endpoint.
Supported AWS Regions
S3 Express One Zone is available in select regions. Spice automatically derives the region from zone IDs:
| Zone ID Prefix | Region |
|---|---|
use1 | us-east-1 |
use2 | us-east-2 |
usw1 | us-west-1 |
usw2 | us-west-2 |
euw1 | eu-west-1 |
euw2 | eu-west-2 |
euw3 | eu-west-3 |
euc1 | eu-central-1 |
eun1 | eu-north-1 |
eus1 | eu-south-1 |
apne1 | ap-northeast-1 |
apne2 | ap-northeast-2 |
apse1 | ap-southeast-1 |
apse2 | ap-southeast-2 |
aps1 | ap-south-1 |
sae1 | sa-east-1 |
cac1 | ca-central-1 |
afs1 | af-south-1 |
mes1 | me-south-1 |
See AWS documentation for the complete list of S3 Express One Zone availability zones.
Important Considerations
- Standard S3 not supported: Cayenne currently only supports S3 Express One Zone, not standard S3 buckets.
- Same-AZ optimization: S3 Express One Zone is optimized for same-availability-zone access. For external access, Cayenne uses extended timeouts (5 minutes per request) and retries.
- Bucket auto-creation: When using
cayenne_s3_zone_ids, Spice automatically creates the S3 Express directory bucket if it doesn't exist (requires appropriate IAM permissions). - Metadata locality: Cayenne metadata (SQLite catalog) remains on local disk. Only data files are stored in S3 Express.
Data Type Support
Cayenne (via Vortex) supports most Arrow data types with the following considerations:
Fully Supported Types
- All integer types (
Int8,Int16,Int32,Int64,UInt*) - Floating point (
Float32,Float64) - Boolean
- Utf8 and LargeUtf8 strings
- Binary and LargeBinary
- Timestamps (normalized to Microsecond precision)
- Date32 and Date64
- Lists and FixedSizeLists
- Structs
Automatically Converted Types
| Original Type | Converted To | Notes |
|---|---|---|
Float16 | Float32 | Automatic conversion for Vortex compatibility |
Timestamp(Nanosecond/...) | Timestamp(Microsecond) | Precision normalized |
Unsupported Types
The following types require the unsupported_type_action parameter:
IntervaltypesDurationtypesMaptypesFixedSizeBinary
unsupported_type_action options:
| Value | Behavior |
|---|---|
error | Fail with error (default) |
string | Convert to Utf8 string |
warn | Include as-is with warning (may fail on insert) |
ignore | Skip the column entirely |
acceleration:
engine: cayenne
mode: file
params:
unsupported_type_action: string # Convert unsupported types to strings
Resource Considerations
Resource requirements for Spice Cayenne depend on dataset size, query patterns, and cache configuration.
Memory
Spice Cayenne manages memory efficiently through columnar storage and selective caching. Memory allocation should account for:
| Component | Default | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Runtime overhead | ~500 MB | Fixed baseline for the Spice runtime |
| Footer cache | 128 MB | Increase for datasets with many files (1-10 KB per file) |
| Segment cache | 256 MB | Increase based on hot data volume |
| Query execution | Variable | Depends on query complexity and concurrency |
Example - Memory-constrained environment:
datasets:
- from: s3://my-bucket/data/
name: constrained_data
acceleration:
engine: cayenne
mode: file
params:
cayenne_footer_cache_mb: 64
cayenne_segment_cache_mb: 128
Storage
Spice Cayenne stores data in a columnar format optimized for analytical queries. Storage requirements include:
- Acceleration data: Compressed Vortex files (typically 30-50% of raw data size with btrblocks)
- Metadata: SQLite database for catalog and statistics (~10 MB per 1000 files)
- Temporary files: Query spill files during complex operations
CPU
Query performance scales with available CPU cores. Vortex's columnar format supports parallel decompression and scanning across multiple threads. Allocate sufficient CPU for:
- Query execution parallelism
- Data refresh and compression operations
- Concurrent query workloads
Limitations
Consider the following limitations when using Spice Cayenne acceleration:
- Beta Status: Spice Cayenne is in active development. Configuration options may change between releases.
- File Mode Only: Spice Cayenne only supports
mode: fileand does not support in-memory (mode: memory) acceleration. - S3 Express Only: Standard S3 buckets are not supported for remote storage. Only S3 Express One Zone directory buckets are supported.
- Unsupported Data Types:
Interval,Duration,Map, andFixedSizeBinarytypes requireunsupported_type_actionconfiguration. - No Traditional Indexes: Spice Cayenne does not support explicit index creation via the
indexesconfiguration. Vortex's segment statistics and fast random access encodings provide equivalent or better performance for most point lookup workloads. - No MVCC: Multi-version concurrency control is not yet implemented. Snapshots and time-travel queries are planned for future releases.
- No File Compaction: Automatic file compaction to reclaim space from deleted rows is not yet available.
As a Beta feature, Spice Cayenne should be thoroughly tested in development environments before production deployment. Monitor release notes for updates, breaking changes, and new capabilities.
Example Spicepod
Complete example configuration using Spice Cayenne with performance tuning:
version: v1
kind: Spicepod
name: cayenne-example
runtime:
query:
memory_limit: 4GiB
temp_directory: /tmp/spice
datasets:
# Local file storage example with upsert
- from: s3://source-bucket/analytics/
name: analytics_data
params:
file_format: parquet
time_column: created_at
acceleration:
engine: cayenne
enabled: true
mode: file
primary_key: id
on_conflict:
id: upsert
refresh_mode: append
refresh_check_interval: 1h
params:
cayenne_compression_strategy: btrblocks
cayenne_footer_cache_mb: 256
cayenne_segment_cache_mb: 512
cayenne_target_file_size_mb: 64
sort_columns: created_at,id
retention_sql: DELETE FROM analytics_data WHERE created_at < NOW() - INTERVAL '30 days'
# S3 Express One Zone storage example
- from: kafka:realtime-events
name: realtime_events
acceleration:
engine: cayenne
enabled: true
mode: file
primary_key: event_id
refresh_mode: append
params:
# S3 Express One Zone for low-latency persistence
cayenne_s3_zone_ids: usw2-az1
cayenne_s3_region: us-west-2
cayenne_compression_strategy: zstd # Fast writes for streaming
cayenne_target_file_size_mb: 32 # Smaller files for faster ingestion
Related Documentation
Spice Documentation:
- Performance Tuning - Comprehensive performance optimization guide
- Managing Memory Usage - Memory configuration reference
- Data Acceleration - Data acceleration overview
External References:
- Apache DataFusion - Query execution engine
- DataFusion Configuration - DataFusion settings and tuning
- Vortex Project - Columnar file format
- Vortex Benchmarks - Performance benchmarks
- FSST Paper - Fast Static Symbol Table compression
- FastLanes Paper - High-performance integer encoding
- ALP Paper - Adaptive floating-point compression
- BtrBlocks Paper - Compression algorithm
- AWS S3 Express One Zone - Low-latency object storage
