Snowflake Data Connector
The Snowflake Data Connector enables federated SQL queries across datasets in the Snowflake Cloud Data Warehouse.
datasets:
- from: snowflake:DATABASE.SCHEMA.TABLE
name: table
params:
snowflake_warehouse: COMPUTE_WH
snowflake_role: accountadmin
Unquoted table identifiers should be UPPERCASED in the from field. See Identifier resolution.
Configuration
from
A Snowflake fully qualified table name (database.schema.table). For instance snowflake:SNOWFLAKE_SAMPLE_DATA.TPCH_SF1.LINEITEM or snowflake:TAXI_DATA."2024".TAXI_TRIPS
name
The dataset name. This will be used as the table name within Spice. The dataset name cannot be a [reserved keyword(../../reference/spicepod/keywords) or any of the following keywords that are reserved by Snowflake:
STARTCONNECTMATCH_RECOGNIZESAMPLETABLESAMPLEFROM
params
| Parameter Name | Description |
|---|---|
snowflake_warehouse | Optional, specifies the Snowflake Warehouse to use |
snowflake_role | Optional, specifies the role to use for accessing Snowflake data |
snowflake_account | Required, specifies the Snowflake account-identifier |
snowflake_username | Required, specifies the Snowflake username to use for accessing Snowflake data |
snowflake_password | Optional, specifies the Snowflake password to use for accessing Snowflake data |
snowflake_private_key_path | Optional, specifies the path to Snowflake private key |
snowflake_private_key_passphrase | Optional, specifies the Snowflake private key passphrase |
Auth
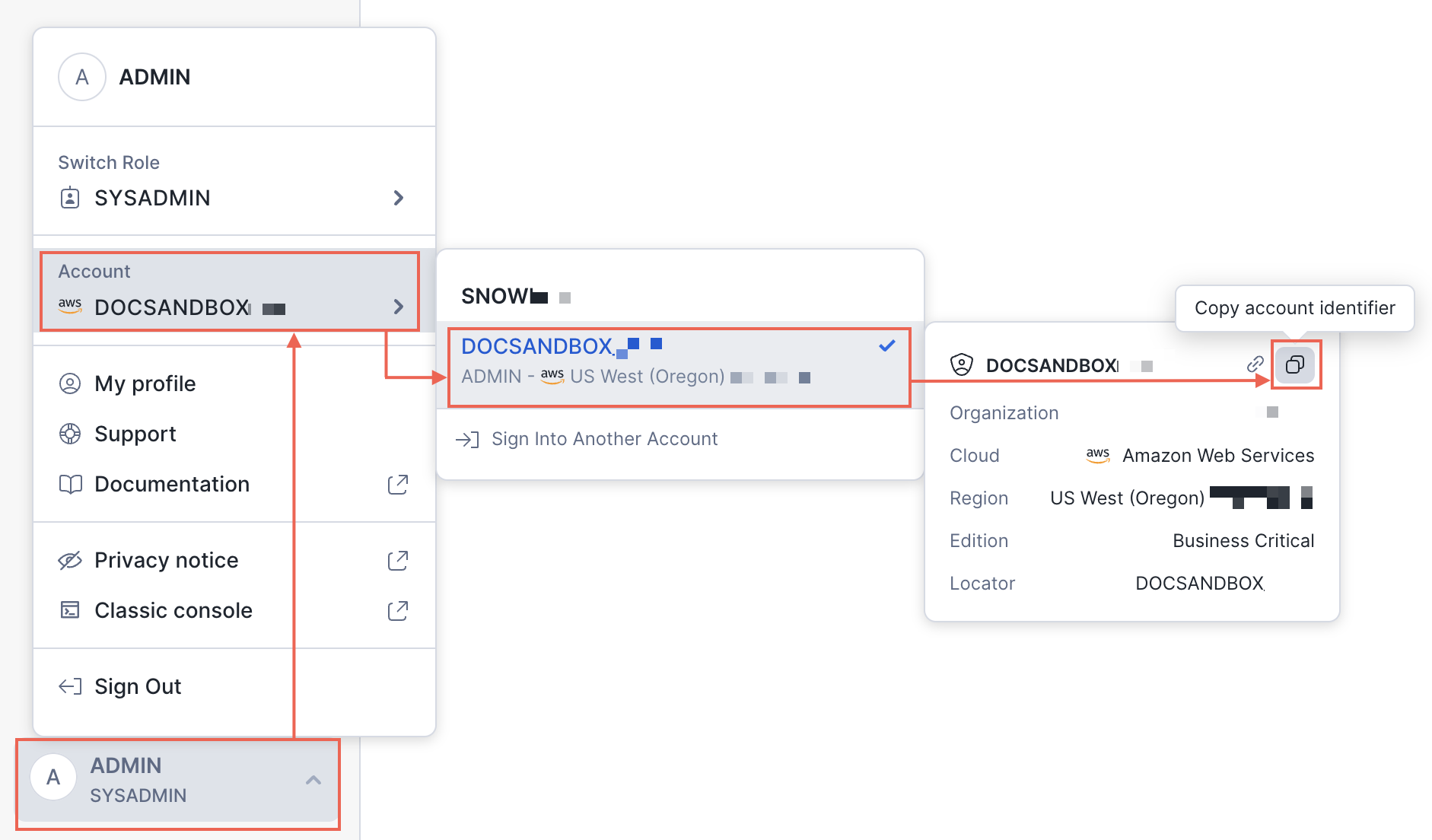
The connector supports password-based and key-pair authentication that must be configured using spice login snowflake or using [Secrets Stores(../secret-stores). Login requires the account identifier ('orgname-accountname' format) - use Finding the organization and account name for an account instructions.
- Env
- Kubernetes
# Password-based
SPICE_SECRET_SNOWFLAKE_ACCOUNT=<account-identifier> \
SPICE_SECRET_SNOWFLAKE_USERNAME=<username> \
SPICE_SECRET_SNOWFLAKE_PASSWORD=<password> \
spice run
# Key-pair (the `<private-key-passphrase>` is an optional parameter and is used for encrypted private key only)
SPICE_SECRET_SNOWFLAKE_ACCOUNT=<account-identifier> \
SPICE_SECRET_SNOWFLAKE_USERNAME=<username> \
SPICE_SECRET_SNOWFLAKE_SNOWFLAKE_PRIVATE_KEY_PATH=<path-to-private-key> \
SPICE_SECRET_SNOWFLAKE_SNOWFLAKE_PRIVATE_KEY_PASSPHRASE=<private-key-passphrase> \
spice run
or using the Spice CLI:
# Password-based
spice login snowflake -a <account-identifier> -u <username> -p <password>
# Key-pair (the `<private-key-passphrase>` is an optional parameter and is used for encrypted private key only)
spice login snowflake -a <account-identifier> -u <username> -k <path-to-private-key> -s <private-key-passphrase>
The CLI will create or update an .env file that looks like:
SPICE_SNOWFLAKE_ACCOUNT="account"
SPICE_SNOWFLAKE_PASSWORD="pass"
SPICE_SNOWFLAKE_USERNAME="user"
Configure the spicepod to load secrets from the env secret store: (Note: This is the default setting)
spicepod.yaml
version: v1
kind: Spicepod
name: spice-app
secrets:
- from: env
name: env
datasets:
- from: snowflake:DATABASE.SCHEMA.TABLE
name: table
params:
snowflake_warehouse: COMPUTE_WH
snowflake_role: accountadmin
snowflake_username: ${env:SPICE_SNOWFLAKE_USERNAME}
snowflake_password: ${env:SPICE_SNOWFLAKE_PASSWORD}
snowflake_account: ${env:SPICE_SNOWFLAKE_ACCOUNT}
Learn more about [Env Secret Store(../secret-stores/env).
# Password-based
kubectl create secret generic snowflake \
--from-literal=account='<account-identifier>' \
--from-literal=username='<username>' \
--from-literal=password='<password>'
# Key-pair (the `<private-key-passphrase>` is an optional parameter and is used for encrypted private key only)
kubectl create secret generic snowflake \
--from-literal=account='<account-identifier>' \
--from-literal=username='<username>' \
--from-literal=snowflake_private_key_path='<path-to-private-key>' \
--from-literal=snowflake_private_key_passphrase='<private-key-passphrase>'
spicepod.yaml
version: v1
kind: Spicepod
name: spice-app
secrets:
- from: kubernetes:snowflake
name: snowflake
datasets:
- from: snowflake:DATABASE.SCHEMA.TABLE
name: table
params:
snowflake_warehouse: COMPUTE_WH
snowflake_role: accountadmin
snowflake_username: ${snowflake.username}
snowflake_password: ${snowflake.password}
snowflake_account: ${snowflake.account}
spicepod.yaml (key-pair with private key content from secret)
version: v1
kind: Spicepod
name: spice-app
secrets:
- from: kubernetes:snowflake
name: snowflake
datasets:
- from: snowflake:DATABASE.SCHEMA.TABLE
name: table
params:
snowflake_warehouse: COMPUTE_WH
snowflake_role: accountadmin
snowflake_auth_type: keypair
snowflake_username: ${snowflake:username}
snowflake_private_key: ${snowflake:private_key}
snowflake_account: ${snowflake:account}
` ```
Learn more about [Kubernetes Secret Store(../secret-stores/kubernetes).
</TabItem>
<TabItem value="keyring" label="Keyring">
Add new keychain entries (macOS) for user and password:
```bash
# Password-based
security add-generic-password -l "Snowflake Secret" \
-a spiced -s spice_snowflake_password\
-w <password>
# Key-pair (the `<private-key-passphrase>` is an optional parameter and is used for encrypted private key only)
security add-generic-password -l "Snowflake Secret" \
-a spiced -s spice_snowflake_snowflake_private_key_path\
-w $(echo -n '<path-to-private-key>' | base64)
spicepod.yaml
version: v1
kind: Spicepod
name: spice-app
secrets:
- from: keyring
name: keyring
datasets:
- from: snowflake:DATABASE.SCHEMA.TABLE
name: table
params:
snowflake_warehouse: COMPUTE_WH
snowflake_role: accountadmin
snowflake_username: user_name
snowflake_password: ${keyring:spice_snowflake_password}
snowflake_account: account_identifier
Learn more about [Keyring Secret Store(../secret-stores/keyring).
Example
datasets:
- from: snowflake:SNOWFLAKE_SAMPLE_DATA.TPCH_SF1.LINEITEM
name: lineitem
params:
snowflake_warehouse: COMPUTE_WH
snowflake_role: accountadmin
- Account identifier does not support the Legacy account locator in a region format. Use Snowflake preferred name in organization format.
- The connector supports password-based and key-pair authentication.
Secrets
Spice integrates with multiple secret stores to help manage sensitive data securely. For detailed information on supported secret stores, refer to the [secret stores documentation(../secret-stores). Additionally, learn how to use referenced secrets in component parameters by visiting the [using referenced secrets guide(../secret-stores#using-secrets).
Cookbook
- A cookbook recipe to configure Snowflake as a data connector in Spice. Snowflake Data Connector
