Spice v1.11.0 (Jan 28, 2026)
Announcing the release of Spice v1.11.0-stable! ⚡
In Spice v1.11.0, Spice Cayenne reaches Beta status with acceleration snapshots, Key-based deletion vectors, and Amazon S3 Express One Zone support. DataFusion has been upgraded to v51 along with Arrow v57.2, and iceberg-rust v0.8.0. v1.11 adds several DynamoDB & DynamoDB Streams improvements such as JSON nesting, and adds significant improvements to Distributed Query with active-active schedulers and mTLS for enterprise-grade high-availability and secure cluster communication.
This release also adds new SMB, NFS, and ScyllaDB Data Connectors (Alpha), Prepared Statements with full SDK support (gospice, spice-rs, spice-dotnet, spice-java, spice.js, and spicepy), Google LLM Support for expanded AI inference capabilities, and significant improvements to caching, observability, and Hash Indexing for Arrow Acceleration.
What's New in v1.11.0
Spice Cayenne Accelerator Reaches Beta
Spice Cayenne has been promoted to Beta status with acceleration snapshots support and numerous performance and stability improvements.
Key Enhancements:
- Key-based Deletion Vectors: Improved deletion vector support using key-based lookups for more efficient data management and faster delete operations. Key-based deletion vectors are more memory-efficient than positional vectors for sparse deletions.
- S3 Express One Zone Support: Store Cayenne data files in S3 Express One Zone for single-digit millisecond latency, ideal for latency-sensitive query workloads that require persistence.
Improved Reliability:
- Resolved
FuturesUnorderedreentrant drop crashes - Fixed memory growth issues related to Vortex metrics allocation
- Metadata catalog now properly respects
cayenne_file_pathlocation - Added warnings for unparseable configuration values
For more details, refer to the Cayenne Documentation.
DataFusion v51 Upgrade
Apache DataFusion has been upgraded to v51, bringing significant performance improvements, new SQL features, and enhanced observability.

Performance Improvements:
- Faster
CASEExpression Evaluation: Expressions now short-circuit earlier, reuse partial results, and avoid unnecessary scattering, speeding up common ETL patterns - Better Defaults for Remote Parquet Reads: DataFusion now fetches the last 512KB of Parquet files by default, typically avoiding 2 I/O requests per file
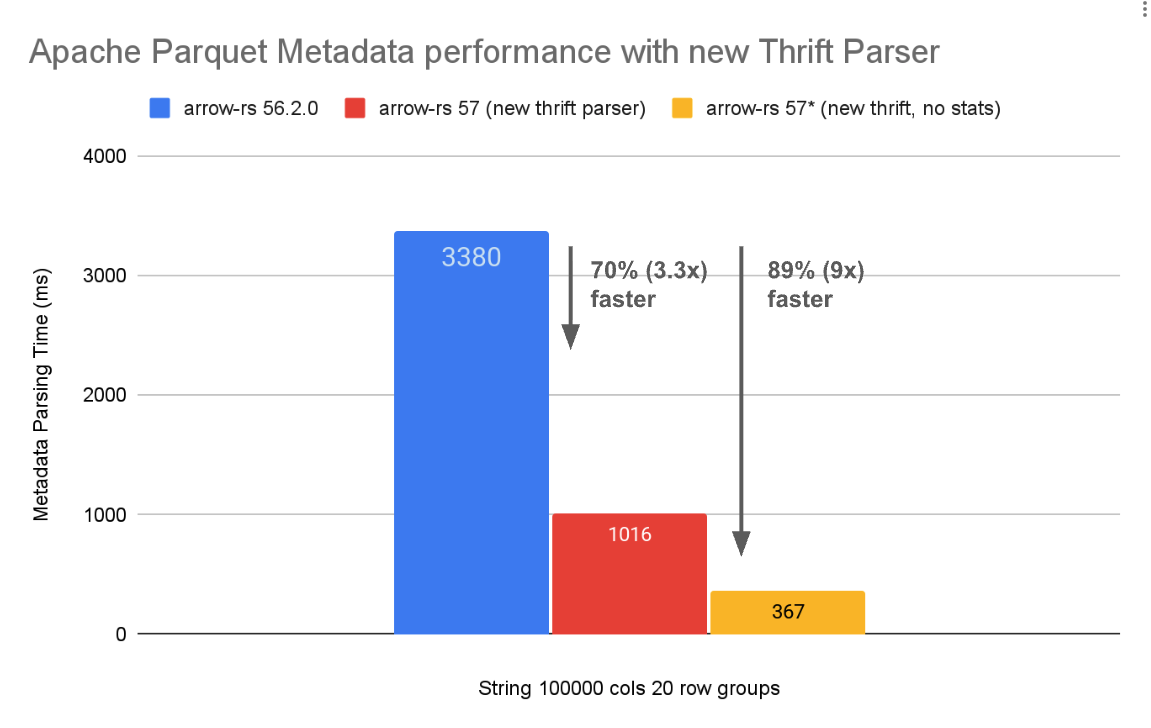
- Faster Parquet Metadata Parsing: Leverages Arrow 57's new thrift metadata parser for up to 4x faster metadata parsing
New SQL Features:
- SQL Pipe Operators: Support for
|>syntax for inline transforms DESCRIBE <query>: Returns the schema of any query without executing it- Named Arguments in SQL Functions: PostgreSQL-style
param => valuesyntax for scalar, aggregate, and window functions - Decimal32/Decimal64 Support: New Arrow types supported including aggregations like
SUM,AVG, andMIN/MAX
Example pipe operator:
SELECT * FROM t
|> WHERE a > 10
|> ORDER BY b
|> LIMIT 5;
Improved Observability:
- Improved
EXPLAIN ANALYZEMetrics: New metrics includingoutput_bytes,selectivityfor filters,reduction_factorfor aggregates, and detailed timing breakdowns
Arrow 57.2 Upgrade
Apache Arrow has been upgraded to v57.2, bringing major performance improvements and new capabilities.
Key Features:
- 4x Faster Parquet Metadata Parsing: A rewritten thrift metadata parser delivers up to 4x faster metadata parsing, especially beneficial for low-latency use cases and files with large amounts of metadata
- Parquet Variant Support: Experimental support for reading and writing the new Parquet Variant type for semi-structured data, including shredded variant values
- Parquet Geometry Support: Read and write support for Parquet Geometry types (
GEOMETRYandGEOGRAPHY) withGeospatialStatistics - New
arrow-avroCrate: Efficient conversion between Apache Avro and ArrowRecordBatches with projection pushdown and vectorized execution support
DynamoDB Connector Enhancements
- Added JSON nesting for DynamoDB Streams
- Improved batch deletion handling
Distributed Query Improvements
High Availability Clusters: Spice now supports running multiple active schedulers in an active/active configuration for production deployments. This eliminates the scheduler as a single point of failure and enables graceful handling of node failures.
- Multiple schedulers run simultaneously, each capable of accepting queries
- Schedulers coordinate via a shared S3-compatible object store
- Executors discover all schedulers automatically
- A load balancer distributes client queries across schedulers
Example HA configuration:
runtime:
scheduler:
state_location: s3://my-bucket/spice-cluster
params:
region: us-east-1
mTLS Verification: Cluster communication between scheduler and executors now supports mutual TLS verification for enhanced security.
Credential Propagation: S3, ABFS, and GCS credentials are now automatically propagated to executors in cluster mode, enabling access to cloud storage across the distributed query cluster.
Improved Resilience:
- Exponential backoff for scheduler disconnection recovery
- Increased gRPC message size limit from 16MB to 100MB for large query plans
- HTTP health endpoint for cluster executors
- Automatic executor role inference when
--scheduler-addressis provided
For more details, refer to the Distributed Query Documentation.
iceberg-rust v0.8.0 Upgrade
Spice has been upgraded to iceberg-rust v0.8.0, bringing improved Iceberg table support.
Key Features:
- V3 Metadata Support: Full support for Iceberg V3 table metadata format
INSERT INTOPartitioned Tables: DataFusion integration now supports inserting data into partitioned Iceberg tables- Improved Delete File Handling: Better support for position and equality delete files, including shared delete file loading and caching
- SQL Catalog Updates: Implement
update_tableandregister_tablefor SQL catalog - S3 Tables Catalog: Implement
update_tablefor S3 Tables catalog - Enhanced Arrow Integration: Convert Arrow schema to Iceberg schema with auto-assigned field IDs,
_filecolumn support, andDate32type support
Acceleration Snapshots
Acceleration snapshots enable point-in-time recovery and data versioning for accelerated datasets. Snapshots capture the state of accelerated data at specific points, allowing for fast bootstrap recovery and rollback capabilities.
Key Features:
- Flexible Triggers: Configure when snapshots are created based on time intervals or stream batch counts
- Automatic Compaction: Reduce storage overhead by compacting older snapshots (DuckDB only)
- Bootstrap Integration: Snapshots can reset cache expiry on load for seamless recovery (DuckDB with Caching refresh mode)
- Smart Creation Policies: Only create snapshots when data has actually changed
Example configuration:
datasets:
- from: s3://my-bucket/data.parquet
name: my_dataset
acceleration:
enabled: true
engine: cayenne
mode: file
snapshots: enabled
snapshots_trigger: time_interval
snapshots_trigger_threshold: 1h
snapshots_creation_policy: on_changed
Snapshots API and CLI: New API endpoints and CLI commands for managing snapshots programmatically.
CLI Commands:
# List all snapshots for a dataset
spice acceleration snapshots taxi_trips
# Get details of a specific snapshot
spice acceleration snapshot taxi_trips 3
# Set the current snapshot for rollback (requires runtime restart)
spice acceleration set-snapshot taxi_trips 2
HTTP API Endpoints:
| Method | Endpoint | Description |
|---|---|---|
| GET | /v1/datasets/{dataset}/acceleration/snapshots | List all snapshots for a dataset |
| GET | /v1/datasets/{dataset}/acceleration/snapshots/{id} | Get details of a specific snapshot |
| POST | /v1/datasets/{dataset}/acceleration/snapshots/current | Set the current snapshot for rollback |
For more details, refer to the Acceleration Snapshots Documentation.
Caching Acceleration Mode Improvements
The Caching Acceleration Mode introduced in v1.10.0 has received significant performance optimizations and reliability fixes in this release.
Performance Optimizations:
- Non-blocking Cache Writes: Cache misses no longer block query responses. Data is written to the cache asynchronously after the query returns, reducing query latency for cache miss scenarios.
- Batch Cache Writes: Multiple cache entries are now written in batches rather than individually, significantly improving write throughput for high-volume cache operations.
Reliability Fixes:
- Correct SWR Refresh Behavior: The stale-while-revalidate (SWR) pattern now correctly refreshes only the specific entries that were accessed instead of refreshing all stale rows in the dataset. This prevents unnecessary source queries and reduces load on upstream data sources.
- Deduplicated Refresh Requests: Fixed an issue where JSON array responses could trigger multiple redundant refresh operations. Refresh requests are now properly deduplicated.
- Fixed Cache Hit Detection: Resolved an issue where queries that didn't include
fetched_atin their projection would always result in cache misses, even when cached data was available. - Unfiltered Query Optimization:
SELECT *queries without filters now return cached data directly without unnecessary filtering overhead.
For more details, refer to the Caching Acceleration Mode Documentation.
Prepared Statements
Improved Query Performance and Security: Spice now supports prepared statements, enabling parameterized queries that improve both performance through query plan caching and security by preventing SQL injection attacks.
Key Features:
- Query Plan Caching: Prepared statements cache query plans, reducing planning overhead for repeated queries
- SQL Injection Prevention: Parameters are safely bound, preventing SQL injection vulnerabilities
- Arrow Flight SQL Support: Full prepared statement support via Arrow Flight SQL protocol
SDK Support:
| SDK | Support | Min Version | Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| gospice (Go) | ✅ Full | v8.0.0+ | SqlWithParams() with typed constructors (Int32Param, StringParam, TimestampParam, etc.) |
| spice-rs (Rust) | ✅ Full | v3.0.0+ | query_with_params() with RecordBatch parameters |
| spice-dotnet (.NET) | ✅ Full | v0.3.0+ | QueryWithParams() with typed parameter builders |
| spice-java (Java) | ✅ Full | v0.5.0+ | queryWithParams() with typed Param constructors (Param.int64(), Param.string(), etc.) |
| spice.js (JavaScript) | ✅ Full | v3.1.0+ | query() with parameterized query support |
| spicepy (Python) | ✅ Full | v3.1.0+ | query() with parameterized query support |
Example (Go):
import "github.com/spiceai/gospice/v8"
client, _ := spice.NewClient()
defer client.Close()
// Parameterized query with typed parameters
results, _ := client.SqlWithParams(ctx,
"SELECT * FROM products WHERE price > $1 AND category = $2",
spice.Float64Param(10.0),
spice.StringParam("electronics"),
)
Example (Java):
import ai.spice.SpiceClient;
import ai.spice.Param;
import org.apache.arrow.adbc.core.ArrowReader;
try (SpiceClient client = new SpiceClient()) {
// With automatic type inference
ArrowReader reader = client.queryWithParams(
"SELECT * FROM products WHERE price > $1 AND category = $2",
10.0, "electronics");
// With explicit typed parameters
ArrowReader reader = client.queryWithParams(
"SELECT * FROM products WHERE price > $1 AND category = $2",
Param.float64(10.0),
Param.string("electronics"));
}
For more details, refer to the Parameterized Queries Documentation.
Spice Java SDK v0.5.0
Parameterized Query Support for Java: The Spice Java SDK v0.5.0 introduces parameterized queries using ADBC (Arrow Database Connectivity), providing a safer and more efficient way to execute queries with dynamic parameters.
Key Features:
- SQL Injection Prevention: Parameters are safely bound, preventing SQL injection vulnerabilities
- Automatic Type Inference: Java types are automatically mapped to Arrow types (e.g.,
double→Float64,String→Utf8) - Explicit Type Control: Use the new
Paramclass with typed factory methods (Param.int64(),Param.string(),Param.decimal128(), etc.) for precise control over Arrow types - Updated Dependencies: Apache Arrow Flight SQL upgraded to 18.3.0, plus new ADBC driver support
Example:
import ai.spice.SpiceClient;
import ai.spice.Param;
try (SpiceClient client = new SpiceClient()) {
// With automatic type inference
ArrowReader reader = client.queryWithParams(
"SELECT * FROM taxi_trips WHERE trip_distance > $1 LIMIT 10",
5.0);
// With explicit typed parameters for precise control
ArrowReader reader = client.queryWithParams(
"SELECT * FROM orders WHERE order_id = $1 AND amount >= $2",
Param.int64(12345),
Param.decimal128(new BigDecimal("99.99"), 10, 2));
}
Maven:
<dependency>
<groupId>ai.spice</groupId>
<artifactId>spiceai</artifactId>
<version>0.5.0</version>
</dependency>
For more details, refer to the Spice Java SDK Repository.
Google LLM Support
Expanded AI Provider Support: Spice now supports Google embedding and chat models via the Google AI provider, expanding the available LLM options for AI inference workloads alongside existing providers like OpenAI, Anthropic, and AWS Bedrock.
Key Features:
- Google Chat Models: Access Google's Gemini models for chat completions
- Google Embeddings: Generate embeddings using Google's text embedding models
- Unified API: Use the same OpenAI-compatible API endpoints for all LLM providers
Example spicepod.yaml configuration:
models:
- from: google:gemini-2.0-flash
name: gemini
params:
google_api_key: ${secrets:GOOGLE_API_KEY}
embeddings:
- from: google:text-embedding-004
name: google_embeddings
params:
google_api_key: ${secrets:GOOGLE_API_KEY}
For more details, refer to the Google LLM Documentation (see docs PR #1286).
URL Tables
Query data sources directly via URL in SQL without prior dataset registration. Supports S3, Azure Blob Storage, and HTTP/HTTPS URLs with automatic format detection and partition inference.
Supported Patterns:
- Single files:
SELECT * FROM 's3://bucket/data.parquet' - Directories/prefixes:
SELECT * FROM 's3://bucket/data/' - Glob patterns:
SELECT * FROM 's3://bucket/year=*/month=*/data.parquet'
Key Features:
- Automatic file format detection (Parquet, CSV, JSON, etc.)
- Hive-style partition inference with filter pushdown
- Schema inference from files
- Works with both SQL and DataFrame APIs
Example with hive partitioning:
-- Partitions are automatically inferred from paths
SELECT * FROM 's3://bucket/data/' WHERE year = '2024' AND month = '01'
Enable via spicepod.yml:
runtime:
params:
url_tables: enabled
Cluster Mode Async Query APIs (experimental)
New asynchronous query APIs for long-running queries in cluster mode:
/v1/queriesendpoint: Submit queries and retrieve results asynchronously
OpenTelemetry Improvements
Unified Telemetry Endpoint: OTel metrics ingestion has been consolidated to the Flight port (50051), simplifying deployment by removing the separate OTel port (50052). The push-based metrics exporter continues to support integration with OpenTelemetry collectors.
Note: This is a breaking change. Update your configurations if you were using the dedicated OTel port 50052. Internal cluster communication now uses port 50052 exclusively.
Observability Improvements
Enhanced Dashboards: Updated Grafana and Datadog example dashboards with:
- Snapshot monitoring widgets
- Improved accelerated datasets section
- Renamed ingestion lag charts for clarity
Additional Histogram Buckets: Added more buckets to histogram metrics for better latency distribution visibility.
For more details, refer to the Monitoring Documentation.
Hash Indexing for Arrow Acceleration (experimental)
Arrow-based accelerations now support hash indexing for faster point lookups on equality predicates. Hash indexes provide O(1) average-case lookup performance for columns with high cardinality.
Features:
- Primary key hash index support
- Secondary index support for non-primary key columns
- Composite key support with proper null value handling
Example configuration:
datasets:
- from: postgres:users
name: users
acceleration:
enabled: true
engine: arrow
primary_key: user_id
indexes:
'(tenant_id, user_id)': unique # Composite hash index
For more details, refer to the Hash Index Documentation.
SMB and NFS Data Connectors
Network-Attached Storage Connectors: New data connectors for SMB (Server Message Block) and NFS (Network File System) protocols enable direct federated queries against network-attached storage without requiring data movement to cloud object stores.
Key Features:
- SMB Protocol Support: Connect to Windows file shares and Samba servers with authentication support
- NFS Protocol Support: Connect to Unix/Linux NFS exports for direct data access
- Federated Queries: Query Parquet, CSV, JSON, and other file formats directly from network storage with full SQL support
- Acceleration Support: Accelerate data from SMB/NFS sources using DuckDB, Spice Cayenne, or other accelerators
Example spicepod.yaml configuration:
datasets:
# SMB share
- from: smb://fileserver/share/data.parquet
name: smb_data
params:
smb_username: ${secrets:SMB_USER}
smb_password: ${secrets:SMB_PASS}
# NFS export
- from: nfs://nfsserver/export/data.parquet
name: nfs_data
For more details, refer to the Data Connectors Documentation.
ScyllaDB Data Connector
A new data connector for ScyllaDB, the high-performance NoSQL database compatible with Apache Cassandra. Query ScyllaDB tables directly or accelerate them for faster analytics.
Example configuration:
datasets:
- from: scylladb:my_keyspace.my_table
name: scylla_data
acceleration:
enabled: true
engine: duckdb
For more details, refer to the ScyllaDB Data Connector Documentation.
Flight SQL TLS Connection Fixes
TLS Connection Support: Fixed TLS connection issues when using grpc+tls:// scheme with Flight SQL endpoints. Added support for custom CA certificate files via the new flightsql_tls_ca_certificate_file parameter.
Developer Experience Improvements
- Turso v0.3.2 Upgrade: Upgraded Turso accelerator for improved performance and reliability
- Rust 1.91 Upgrade: Updated to Rust 1.91 for latest language features and performance improvements
- Spice Cloud CLI: Added
spice cloudCLI commands for cloud deployment management - Improved Spicepod Schema: Improved JSON schema generation for better IDE support and validation
- Acceleration Snapshots: Added configurable
snapshots_create_intervalfor periodic acceleration snapshots independent of refresh cycles - Tiered Caching with Localpod: The Localpod connector now supports
cachingrefresh mode, enabling multi-layer acceleration where a persistent cache feeds a fast in-memory cache - GitHub Data Connector: Added workflows and workflow runs support for GitHub repositories
- NDJSON/LDJSON Support: Added support for Newline Delimited JSON and Line Delimited JSON file formats
Additional Improvements & Bug Fixes
- Model Listing: New functionality to list available models across multiple AI providers
- DuckDB Partitioned Tables: Primary key constraints now supported in partitioned DuckDB table mode
- Post-refresh Sorting: New
on_refresh_sort_columnsparameter for DuckDB enables data ordering after writes - Improved Install Scripts: Removed jq dependency and improved cross-platform compatibility
- Better Error Messages: Improved error messaging for bucket UDF arguments and deprecated OpenAI parameters
- Reliability: Fixed DynamoDB IAM role authentication with new
dynamodb_auth: iam_roleparameter - Reliability: Fixed cluster executors to use scheduler's
temp_directoryparameter for shuffle files - Reliability: Initialize secrets before object stores in cluster executor mode
- Reliability: Added page-level retry with backoff for transient GitHub GraphQL errors
- Performance: Improved statistics for rewritten
DistributeFileScanOptimizerplans - Developer Experience: Added
max_message_sizeconfiguration for Flight service
Contributors
Breaking Changes
OTel Ingestion Port Change
OTel ingestion has been moved to the Flight port (50051), removing the separate OTel port 50052. Port 50052 is now used exclusively for internal cluster communication. Update your configurations if you were using the dedicated OTel port.
Distributed Query Cluster Mode Requires mTLS
Distributed query cluster mode now requires mTLS for secure communication between cluster nodes. This is a security enhancement to prevent unauthorized nodes from joining the cluster and accessing secrets.
Migration Steps:
- Generate certificates using
spice cluster tls initandspice cluster tls add - Update scheduler and executor startup commands with
--node-mtls-*arguments - For development/testing, use
--allow-insecure-connectionsto opt out of mTLS
Renamed CLI Arguments:
| Old Name | New Name |
|---|---|
--cluster-mode | --role |
--cluster-ca-certificate-file | --node-mtls-ca-certificate-file |
--cluster-certificate-file | --node-mtls-certificate-file |
--cluster-key-file | --node-mtls-key-file |
--cluster-address | --node-bind-address |
--cluster-advertise-address | --node-advertise-address |
--cluster-scheduler-url | --scheduler-address |
Removed CLI Arguments:
--cluster-api-key: Replaced by mTLS authentication
Cookbook Updates
New ScyllaDB Data Connector Recipe: New recipe demonstrating how to use the ScyllaDB Data Connector. See ScyllaDB Data Connector Recipe for details.
New SMB Data Connector Recipe: New recipe demonstrating how to use the SMB Data Connector. See SMB Data Connector Recipe for details.
The Spice Cookbook includes 86 recipes to help you get started with Spice quickly and easily.
Upgrading
To upgrade to v1.11.0, use one of the following methods:
CLI:
spice upgrade
Homebrew:
brew upgrade spiceai/spiceai/spice
Docker:
Pull the spiceai/spiceai:1.11.0 image:
docker pull spiceai/spiceai:1.11.0
For available tags, see DockerHub.
Helm:
helm repo update
helm upgrade spiceai spiceai/spiceai --version 1.11.0
AWS Marketplace:
Spice is available in the AWS Marketplace.
Dependencies
- DataFusion: Upgraded to v51 (release notes)
- Arrow: Upgraded to v57.2 (release notes)
- iceberg-rust: Upgraded to v0.8.0 (release notes)
What's Changed
Changelog
- OTel exporter for push metrics by @lukekim in #8442
- fix: Update benchmark snapshots by @app/github-actions in #8448
- Add TPCH append tests to scheduled dispatch workflow by @sgrebnov in #8451
- Add snapshot creation logging by @krinart in #8469
- Fix PeriodicReader panic by @krinart in #8471
- Benchmarks: increase readiness timeout for turso acceleration (TPC-H) by @sgrebnov in #8470
- fix: Pin CUDA build actions to commits by @peasee in #8477
- Add Criterion benchmarking to
chunkingcrate. by @Jeadie in #8431 - DuckDB agg pushdown: gate behind accelerator parameter by @mach-kernel in #8474
- Rename
aggregate_pushdown_optimization->optimizer_duckdb_aggregate_pushdownby @ewgenius in #8485 - Handle throttling exception for DynamoDB streams by @phillipleblanc in #8492
- docs: Add release notes by @peasee in #8478
- Update spicepod.schema.json by @app/github-actions in #8496
- Move 'test_projection_pushdown' to
runtime-datafusionby @Jeadie in #8490 - Fix OTEL metrics HTTP exporter client setup by @phillipleblanc in #8489
- Update endgame to include new caching accelerator cookbook by @phillipleblanc in #8487
- DynamoDB tests and fixes by @lukekim in #8491
- Align
make lint-rust-fixwithmake lint-rustby @Jeadie in #8499 - fix: Remove unused Cayenne parameters by @peasee in #8500
- Force task history
captured_planoutputs to be captured even if they would be filtered out otherwise by @phillipleblanc in #8501 - release: post-release updates by @peasee in #8503
- CI: Fix E2E models dispatch by @mach-kernel in #8505
- Use an isolated Tokio runtime for refresh tasks that is separate from the main query API by @phillipleblanc in #8504
- Update openapi.json by @app/github-actions in #8512
- Update dependencies by @phillipleblanc in #8513
- fix: Avoid double hashing cache key by @peasee in #8511
- fix: Eagerly drop cached records for results larger than max by @peasee in #8516
- feat: Support vortex zstd compressor by @peasee in #8515
- warning if column is defined in spicepod but is non-existant by @Jeadie in #8498
- Return summarized spicepods from /v1/spicepods by @phillipleblanc in #8404
- Fix for idle DynamoDB Stream by @krinart in #8506
- Use
Datafusion::PlanoverDatafusion::Internalfor user-facing search errors. by @Jeadie in #8484 - DDB Streams Integration Test + Memory Acceleration + Improved Warning by @krinart in #8520
- Upgrade to gospice v8 by @lukekim in #8524
- Vortex file format for object store by @Jeadie in #8525
- docs: Add missing cookbooks to endgame, focus area section by @peasee in #8527
- ListingTableConnector: Drop partition columns that reoccur in file schema by @mach-kernel in #8519
- fix(cluster): initialize secrets before object stores in executor by @sgrebnov in #8532
- Use separate Tokio runtime for SWR refreshes by @phillipleblanc in #8530
- fix: SQL Results Cache SWR triggers incorrect cache miss metric by @phillipleblanc in #8529
- feat: testoperator: OTLP streaming metrics / connect to existing instance / infinite mode / query timeout by @phillipleblanc in #8537
- Update openapi.json by @app/github-actions in #8518
- Add better attributes for search testing by @Jeadie in #8531
- fix: Improve Cayenne errors, ID selection for table/partition creation by @peasee in #8523
- Percent-encode Kubernetes secret name path segment by @phillipleblanc in #8522
- Initial parameterisation of Search integration tests by @Jeadie in #8066
- fix: Add warning when multiple partitions are defined for the same table by @peasee in #8540
- Add DuckDB file-mode support for search test parameterization. by @Jeadie in #8541
- fix: Add recursion depth limits to prevent DoS via deeply nested data (DynamoDB + S3 Vectors) by @phillipleblanc in #8544
- Remove the
clippy::too_many_lineslint by @phillipleblanc in #8549 - feat: Add
spice cluster tlscommands by @phillipleblanc in #8550 - Move OTel ingestion to Flight port, remove separate OTel port 50052 by @phillipleblanc in #8551
- Move verbose tool init messages to trace by @phillipleblanc in #8552
- Add SANs to
spice cluster tls addcertificates by @phillipleblanc in #8554 - Add cpu, gpu, and memory to telemetry by @lukekim in #8483
- feat: Add workflows and workflow runs to GitHub Data Connector by @peasee in #8548
- Add S3Vectors option for paramterised search tests by @Jeadie in #8555
- Distributed query: TLS + API key by @mach-kernel in #8468
- Refactor RRF SQL to use LogicalPlanBuilder by @Jeadie in #7968
- Require mTLS for distributed query cluster mode by @phillipleblanc in #8580
- Fix stats for rewritten
DistributeFileScanOptimizerplans by @mach-kernel in #8581 - Bump actions/cache from 4.3.0 to 5.0.1 by @app/dependabot in #8573
- Show user-friendly error on empty DDB table by @krinart in #8586
- Add
(Deprecated)labels to deprecatedspice sqlparams by @krinart in #8588 - Fix kafka warning when
security.protocolis set toPLAINTEXTby @krinart in #8587 - Upgrade dependencies by @phillipleblanc in #8593
- Release notes for v1.10.1 by @Jeadie in #8568
- Run search benchmarks twice a week. by @Jeadie in #8592
- Add cayenne data accelerator by @Jeadie in #8553
- SQL allowlist for tools: sql, list_datasets, search, table_schema by @Jeadie in #8449
- use
rstestfor llms integration tests by @Jeadie in #8566 - Post v1.10.1 housekeeping by @Jeadie in #8600
- Add checklist for SDK publication in end_game.md by @Jeadie in #8602
- Fix IMAGE_TAG assignment for Docker compatibility by @Jeadie in #8599
- Modify cluster arguments to spiced for UX review by @phillipleblanc in #8603
- Update QA analytics with new release data by @Jeadie in #8601
- Remove 'tract-core' dependency. by @Jeadie in #8605
- Google embedding and chat models. by @Jeadie in #8423
- Fix test_github_workflows integration test by @sgrebnov in #8607
- Update openapi.json by @app/github-actions in #8604
- ci: Upload artifacts to MinIO eagerly after each build step by @phillipleblanc in #8615
- fix: SQLite accelerator decimal/date handling by @phillipleblanc in #8606
- Configure mTLS for executor-to-executor gRPC connections by @sgrebnov in #8617
- feat: Enable localpod with caching mode accelerator for tiered caching by @phillipleblanc in #8621
- Add Cayenne S3 Express One Zone support for data files by @lukekim in #8502
- Add snapshot interval for acceleration snapshots by @phillipleblanc in #8627
- Add dataset_load_parallelism parameter to spicepod.yml by @peasee in #8630
- Json Nesting for DynamoDB by @krinart in #8623
- Restore deprecated open-telemetry flag in spiced by @phillipleblanc in #8629
- Implement batching for Kafka/Debezium + null Decimal handling by @krinart in #8622
- fix: Status field in /v1/datasets & /v1/models by @lukekim in #8633
- Add Spice test operator improvements by @sgrebnov in #8625
- Add v1.10.2 release notes by @sgrebnov in #8640
- Align object-store vortex with runtime feature flagging by @Jeadie in #8620
- Extended LLM & search tests on cron by @Jeadie in #8624
- Test-operator: emit main metrics as part of load tests by @sgrebnov in #8639
- Build a local docker image from an existing Spice binary by @phillipleblanc in #8619
- fix: Use runtime-rate-control for GitHub Data Connector by @peasee in #8638
- Upgrade dependencies by @phillipleblanc in #8655
- Bump headers-accept from 0.1.4 to 0.3.0 by @app/dependabot in #8644
- Update openapi.json by @app/github-actions in #8637
- Update SECURITY.md - Include v1.10.2 by @sgrebnov in #8661
- Serialize acceleration snapshots with refresh writes by @phillipleblanc in #8652
- Update AI Installation test to use minilm_l6_v2 by @sgrebnov in #8659
- Fixes for search integration test CI by @Jeadie in #8656
- fix: Use a GitHub rate controller per auth context by @peasee in #8662
- fix: Update Search integration test snapshots by @app/github-actions in #8654
- Make E2E Test Release Installation (AI, Local HF model) test more robust by @sgrebnov in #8666
- Fix issue with location predicate for custom S3 endpoints + regression integration test by @phillipleblanc in #8668
- fix: Validate schema match before projection pushdown in UnionProjectionPushdownOptimizer by @phillipleblanc in #8669
- Proper batch commit for kafka/debezium by @krinart in #8671
- Improve spicepod json schema generation by @ewgenius in #8547
- Start the anonymous telemetry exporter asynchronously by @phillipleblanc in #8679
- fix: Move enforce-pulls to hosted runner by @phillipleblanc in #8686
- Update QA analytics with 1.10.2 release data by @sgrebnov in #8667
- fix: Azure does not support suffix range requests by @phillipleblanc in #8685
- Remove
spicepod-validatorcargo build frombuild-devtarget by @Jeadie in #8684 - fix: Update test snapshots by @app/github-actions in #8680
- fix: Update Search integration test snapshots by @app/github-actions in #8681
- SMB and NFS Data Connectors by @lukekim in #8674
- Upgrade to openai-async v0.32 by @lukekim in #8635
- v1.10.3 release notes by @phillipleblanc in #8693
- Upgrade dependencies by @phillipleblanc in #8704
- fix: Support NDJSON and LDJSON by @lukekim in #8649
- move OpenAI overrides to non-prefixed by @Jeadie in #8678
- Update Google LLM param: google_dimensions -> dimensions by @Jeadie in #8677
- Make cluster mTLS optional with insecure flag by @phillipleblanc in #8703
- Revert "fix: Move enforce-pulls to hosted runner (#8686)" by @phillipleblanc in #8709
- Initial 'testoperator run text-to-sql' by @Jeadie in #8618
- Add support for abfss by @krinart in #8706
- Add testoperator TPCH dispatch for ABFS with hierarchical namespace disabled + versioning enabled by @phillipleblanc in #8711
- Update openapi.json by @app/github-actions in #8692
- cluster: validate --role argument by @phillipleblanc in #8717
- Upgrade to Turso v0.3.2 by @lukekim in #8716
- Rename --insecure to --allow-insecure-connections to be consistent with existing naming by @lukekim in #8720
- Remove 'testoperator run http-consistency/http-overhead' by @Jeadie in #8708
- refactor: Remove cluster feature flag by @phillipleblanc in #8718
- Docs: Distributed query ADR by @mach-kernel in #8608
- Use
model.datasetsto allowlist on tools by @Jeadie in #8714 - cluster: quality of life improvements to starting cluster mode locally by @phillipleblanc in #8719
- Docs: Ballista extension ADR by @mach-kernel in #8616
- Improve deprecation messages when going from prefixed -> non-prefixed. by @Jeadie in #8724
- Remove
toolsfrom auto-defaults by @Jeadie in #8725 - Make distinct providers for vector spilling, vector partitioning. by @Jeadie in #8546
- cluster: default scheduler address port by @phillipleblanc in #8728
- Add Makefile targets for testoperator by @Jeadie in #8729
text-to-sqldispatch in testoperator by @Jeadie in #8705- DR-006: High Availability Distributed Query with Stateless Schedulers by @lukekim in #8721
- DR-007: mTLS for Distributed Query Cluster Communication by @lukekim in #8722
- SMB and NFS improvements by @lukekim in #8710
- fix: Cluster executors use scheduler's temp_directory for shuffle files by @phillipleblanc in #8733
- use 'max_message_size' in flight service too by @Jeadie in #8730
- Add page-level retry for transient GraphQL errors with backoff and increase GitHub rate limit buffer up to 100 by @ewgenius in #8726
- Make testoperator Dockerfile; CI to build docker image to
ghcr.io. by @Jeadie in #8732 - cluster: UnionProjectionPushdownOptimizer: Add projection pushdown diagnostics for union children by @phillipleblanc in #8734
- Fix column projection order mismatch with location metadata columns by @phillipleblanc in #8738
- Fixes for testoperator. by @Jeadie in #8737
- Improve Cayenne Deletion Vectors with KeyBased support by @lukekim in #8713
- Fix
testoperator_dispatch.yamlby @Jeadie in #8740 - Add spice cloud CLI commands by @lukekim in #8528
- Add FTP, NFS, & SMB TPCH SF1 spicepods by @lukekim in #8739
- Prepared Statements by @lukekim in #7588
- Schedule dispatch of
testoperator run text-to-sql. by @Jeadie in #8745 - Fix minio for ai benchmark CI by @Jeadie in #8743
- Upgrade to Rust 1.91 by @phillipleblanc in #8749
- fix: Update benchmark snapshots by @app/github-actions in #8763
- Benchmarks: make row count validation skip logic configurable by scale factor, query set, and overrides by @sgrebnov in #8756
- Make benchmark tests more robust by @sgrebnov in #8766
- Add parameter to force using iam_role for DynamoDB by @krinart in #8767
- fix: Update Search integration test snapshots by @app/github-actions in #8735
- v1.10.4 release notes by @phillipleblanc in #8790
- Trace metrics export errors by @sgrebnov in #8791
- v1.10.4 SECURITY.md update by @phillipleblanc in #8800
- Add timezone database to Docker image to fix Cayenne acceleration panic by @sgrebnov in #8799
- Upgrade dependencies by @phillipleblanc in #8801
- Fix
table_allowlistfor table sampling and NSQL by @Jeadie in #8789 - Cayenne primary key on-conflict handling by @lukekim in #8788
- fix: Update benchmark snapshots by @app/github-actions in #8773
- fix: correctly identify deprecated openai_* parameters by @phillipleblanc in #8809
- fix: Update benchmark snapshots by @app/github-actions in #8812
- Use workspace version for cayenne crate by @phillipleblanc in #8811
- Don't CAST strings which breaks push down optimizer by @lukekim in #8810
- fix: Update benchmark snapshots by @app/github-actions in #8815
- Update async-openai to latest revision 4dcd633aad6f - brings fix for openai compatible model providers by @ewgenius in #8816
- Add
auth/iam_role_sourceto DynamoDB connector by @krinart in #8808 - DynamoDB fixes: JSON nesting for Streams, proper batch deletions by @krinart in #8821
- Rough roadmap for 2026-2027 by @lukekim in #8805
- Release notes for v1.11.0-rc1 by @ewgenius in #8786
- Make S3V integration tests prepare_for_aws_tests more robust by @sgrebnov in #8820
- Bump rsa from 0.9.9 to 0.9.10 in the cargo group across 1 directory by @app/dependabot in #8819
- Add timezone database to Release and CUDA Docker images to fix Cayene panic by @sgrebnov in #8832
- fix:
UnionProjectionPushdownOptimizer- Schema change duringtransform_downbreaks parent nodes by @phillipleblanc in #8831 - Update grafana/datadog example dashboards by @krinart in #8833
- Add Dev bird bench as text-to-sql queryset in CI. by @Jeadie in #8753
- Update testoperator scheduler to use
release/1.11branch by @ewgenius in #8829 - Spice Cayenne fixes and test spicepods for Beta & RC by @lukekim in #8787
- testoperator dispatch all bird-bench database variants by @Jeadie in #8835
- feat: Improve column statistics handling with safe access and defaults by @phillipleblanc in #8836
- cluster: mTLS verification by @phillipleblanc in #8837
- fix: 8770: Unsupported ScalarFunctionExpr in ORDER BY by @lukekim in #8838
- Workflow tweaks by @lukekim in #8845
- Cayenne: metadata catalog should respect cayenne_file_path location by @sgrebnov in #8844
- Expand Cayenne feature coverage by @lukekim in #8848
- docs: HA distributed query decisions by @phillipleblanc in #8817
- fix(optimizer): Fix correctness issues in UnionProjectionPushdownOptimizer by @phillipleblanc in #8851
- Pin reqwest to 0.12.24 to fix HuggingFace embedding model download by @ewgenius in #8853
- Fix builds and pin to Ubuntu 22.04 by @lukekim in #8856
- Revert "Fix builds and pin to Ubuntu 22.04" by @lukekim in #8861
- Ensure setup Rust is run by @lukekim in #8862
- fix: Ubuntu 24.04+ renamed libaio1 to libaio1t64 by @lukekim in #8865
- Upgrade to Pulls with Spice v2 by @lukekim in #8866
- Add limit and configuration name to 'testoperator run text-to-sql' by @Jeadie in #8839
- PR check and test optimization by @lukekim in #8868
- Upgrade S3 Vectors SDK and improve test robustness by @lukekim in #8867
- [Testoperator] Query level and improved aggregate level for NSQL by @Jeadie in #8840
- Add docker build for private branches for ghcr.io/spiceai/spiceai-dev by @phillipleblanc in #8873
- Expand the data acceleration round-trip test coverage by @lukekim in #8855
- fix: Provide a better error for improper bucket UDF arguments by @peasee in #8849
- ScyllaDB Data Connector by @lukekim in #8827
- Use tokio-rusqlite for Spice Cayenne SQLite by @lukekim in #8857
- Cayenne: fix FuturesUnordered reentrant drop crash by @sgrebnov in #8863
- Bump github/codeql-action from 4.31.9 to 4.31.10 by @app/dependabot in #8884
- Bump golang.org/x/sys from 0.39.0 to 0.40.0 by @app/dependabot in #8881
- Bump github.com/spiceai/gospice/v8 from 8.0.0 to 8.0.1 by @app/dependabot in #8883
- Bump roaring from 0.11.2 to 0.11.3 by @app/dependabot in #8885
- Bump golang.org/x/mod from 0.31.0 to 0.32.0 by @app/dependabot in #8882
- Bump aws-sdk-s3 from 1.115.0 to 1.119.0 by @app/dependabot in #8887
- Bump libc from 0.2.177 to 0.2.180 by @app/dependabot in #8886
- Bump tokio-util from 0.7.17 to 0.7.18 by @app/dependabot in #8889
- Bump governor from 0.10.2 to 0.10.4 by @app/dependabot in #8888
- fix: flaky test test_concurrent_partition_creation by @phillipleblanc in #8898
- Update Cayenne snapshots for TPC-DS by @lukekim in #8890
- Add more buckets to histogram metrics by @krinart in #8850
- feat: Add HTTP health endpoint for cluster executors by @phillipleblanc in #8899
- feat: Implement model listing functionality for multiple providers by @lukekim in #8901
- feat: Initial HA schedulers distributed query implementation by @phillipleblanc in #8852
- fix: infer executor role from --scheduler-address when --role is omitted by @phillipleblanc in #8903
- Improve install scripts and remove jq dependency by @lukekim in #8847
- Benchmarks: sort PartitionedUnionExec children for deterministic snapshot comparison by @sgrebnov in #8877
- Cayenne: share VortexFileCache across partitions via CayenneContext by @sgrebnov in #8880
- Update ballista to add exponential backoff for scheduler disconnection by @phillipleblanc in #8905
- Configurably add BirdBench evidence to testoperator text-to-SQL. by @Jeadie in #8904
- Helm: Allow command override via values.yaml by @sgrebnov in #8906
- Fix distributed query gRPC message size limit (16MB -> 100MB) by @phillipleblanc in #8900
- OS specific setup actions by @lukekim in #8909
- Cayenne should warn if unable to parse configuration value by @sgrebnov in #8907
- Add snapshots widgets to example dashboard by @krinart in #8910
- Add quality criteria for the features by @krinart in #8897
- Improve Accelerated Datasets section for Grafana/Datadog dashboards by @krinart in #8915
- Use HTTP traceparent in NSQL to support concurrency in 'testoperator run text-to-SQL' by @Jeadie in #8912
- Remove setup for cc from integration_models.yml by @Jeadie in #8917
- Propagate Azure and GCS credentials to executors in cluster mode by @phillipleblanc in #8918
- Cayenne: fix memory growth due to vortex metrics allocation by @sgrebnov in #8908
- fix(caching): Deduplicate refresh requests for JSON array responses by @sgrebnov in #8921
- fix(caching): Return cached data directly for unfiltered queries (SELECT *) by @sgrebnov in #8919
- Correct MinIO path syntax for spiced download by @Jeadie in #8916
- Acceleration snapshots compaction + Improved Snapshots UX by @krinart in #8858
- Change base image from bookworm-slim to trixie-slim by @Jeadie in #8923
- Add
testoperator run text-to-sqlmetrics from LogicalPlan by @Jeadie in #8895 - Fix spicepod dependencies in testoperator by @Jeadie in #8875
- Update copilot instructions for data correctness by @lukekim in #8922
- Add
BootstrapStatus+ Snapshot bootstrapping parallelization by @krinart in #8926 - fix: add missing feature-gate for AWS Secrets Manager error variant by @phillipleblanc in #8928
- refactor: make ConnectorParams fields public for external connectors by @phillipleblanc in #8929
- fix(caching): SWR refreshes only accessed entry instead of all stale rows by @sgrebnov in #8931
- Cayenne: include
cayenne_metadata_dirto known params by @sgrebnov in #8933 - Rename Ingestion Lag chart in example dashboards by @krinart in #8932
- fix(caching): Fix HTTP caching always MISS when projection excludes fetched_at by @sgrebnov in #8930
- Reset expiry after snapshot bootstraping for Caching by @krinart in #8925
- Set use_ssl=false for sccache by @lukekim in #8945
- Hash indexing for Arrow Acceleration by @lukekim in #8924
- [Cayenne] Acceleration snapshots support by @lukekim in #7973
- perf(caching): Non-blocking cache writes on cache miss by @sgrebnov in #8948
- Update NSQL models by @lukekim in #8951
- Hash Index Key verification by @lukekim in #8949
- Add
snapshots_creation_policyparam by @krinart in #8954 - Remove candle & cudarc from non-models build by @lukekim in #8955
- Acceleration Snapshots API and CLI by @lukekim in #8934
- Ignore test for
data_components arrow::indexed::test_primary_key_value_matches_batchby @Jeadie in #8962 - fix: Update benchmark snapshots by @app/github-actions in #8965
- Hash Index secondary index support by @lukekim in #8958
- fix: Support primary key constraints in partitioned DuckDB tables mode by @sgrebnov in #8966
- perf(caching): Batch cache writes by @sgrebnov in #8959
- CI perf optimizations by @lukekim in #8968
- Fix Makefile linting by @Jeadie in #8970
- Fixes in
testoperator run text-to-sql. by @Jeadie in #8927 - implement
Chat::as_sqlfor xAI anthropic by @Jeadie in #8957 - Fix
duckdb_file_pathin search integration test by @Jeadie in #8972 - fix: Update benchmark snapshots by @app/github-actions in #8971
- Maintenance updates to Anthropic API by @Jeadie in #8956
- Add CacheBackend Trait, implement pingora-lru, and add throughput tests by @lukekim in #8080
- fix: Update benchmark snapshots by @app/github-actions in #8974
- fix: Update benchmark snapshots by @app/github-actions in #8975
- Make accelerator shutdown more robust by @lukekim in #8969
- feat(duckdb): Add
on_refresh_sort_columnsfor post-write data ordering (initial version) by @sgrebnov in #8964 - Proper handling for initial snapshot by @krinart in #8911
- fix: Remove --no-default-features from cargo-hack command in features workflow by @phillipleblanc in #8977
- build(deps): bump actions/cache from 5.0.1 to 5.0.2 by @app/dependabot in #8983
- build(deps): bump actions/checkout from 4 to 6 by @app/dependabot in #8982
- build(deps): bump actions/setup-go from 6.1.0 to 6.2.0 by @app/dependabot in #8984
- build(deps): bump github.com/olekukonko/tablewriter from 1.1.2 to 1.1.3 by @app/dependabot in #8979
- build(deps): bump github.com/klauspost/compress from 1.18.2 to 1.18.3 by @app/dependabot in #8980
- Add /v1/queries and Arrow Flight async APIs by @lukekim in #8946
- build(deps): bump Vampire/setup-wsl from 5 to 6 by @app/dependabot in #8981
- fix: Update Search integration test snapshots by @app/github-actions in #8973
- build(deps): bump insta from 1.46.0 to 1.46.1 by @app/dependabot in #8988
- build(deps): bump schemars from 1.1.0 to 1.2.0 by @app/dependabot in #8985
- fix: Update benchmark snapshots by @app/github-actions in #8978
- fix: Data correctness edge cases by @lukekim in #8953
- Correct MinIO path syntax for spiced download (Part 2) by @Jeadie in #8995
- Make
.spice/datain search integration tests by @Jeadie in #8992 - fix: Hash index composite keys null values by @lukekim in #9001
- Update Cayenne status to Beta by @lukekim in #9002
- fix: Disable TPC-DS result validation (not yet supported) by @sgrebnov in #9004
- feat: Upgrade to DataFusion v51 and dependencies by @lukekim in #8864
- Improvements for
snapshots_creation_policyby @krinart in #9003 - fix(ci): restore cached spicepod-validator binary instead of lookup-only by @phillipleblanc in #9007
- Update version by @krinart in #9010
- Update lock file - https://github.com/spiceai/spiceai/commit/53babbf07ca8c1c7b2e1da42ce58c465d9bc9276/
- fix: Enable Cayenne acceleration snapshots by @lukekim in #9020
- Add TPC-DS integration tests with S3 source and PostgreSQL acceleration by @phillipleblanc in #9006
- fix(tests): fix flaky/slow/failing unit tests by @phillipleblanc in #9009
- fix: Update benchmark snapshots for DF51 upgrade by @app/github-actions in #9008
- fix: add feature gate to rrf TEST_EMBEDDING_MODEL by @phillipleblanc in #9017
- fix: features check by @phillipleblanc in #9014
- URL table support by @lukekim in #9018
- ScyllaDB key filter by @lukekim in #8997
- fix: Schema mismatch when using column projection with HTTP caching by @phillipleblanc in #9021
- Add more tests for HTTP caching with columns selection by @sgrebnov in #9025
- HTTP cache snapshots: default to
time_intervaland fixsnapshots_creation_policy: on_changeby @sgrebnov in #9026 - Fix duplicate snapshot creation on startup by @sgrebnov in #9029
- Remove waiting for runtime to be ready before creating snapshot by @krinart in #9033
- Fix snapshot on_change policy to skip when no writes occurred by @sgrebnov in #9028
- Release notes for release
release/1.11.0-rc.2by @krinart in #9016 - ci: use arduino/setup-protoc for official protobuf compiler by @phillipleblanc in #9036
- ci: install unzip on aarch64 runner for arduino/setup-protoc by @phillipleblanc in #9038
- fix: don't fail release if upload to minio fails by @phillipleblanc in #9039
- Improve validation and logging for hash indexes by @lukekim in #9047
- Pin to ubuntu-22.04 by @lukekim in #9068
- Fix broken telemetry for
testoperatorby @krinart in #9054 - Fix release builds by @lukekim in #9069
- Spice 1.11.0-rc3 release notes by @krinart in #9070
- Update spicepod.schema.json by @app/github-actions in #9071
- Add missing protoc step to setup-cc action by @krinart in #9041
- Fix TLS connection for grpc+tls:// Flight SQL endpoints and add custom CA certificate support by @phillipleblanc in #9073
- Update
1.11.0-rc.3release notes by @krinart in #9082 - Fix
formula_1andcodebase_communityinbird-benchby @Jeadie in #9000 - Cayenne S3 Express One Zone improvements by @lukekim in #9015
- Add zlib1g-dev to CI by @lukekim in #9052
- Upgrade Vortex with CASE-WHEN by @lukekim in #9051
- fix: Cayenne CatalogError handling for constraint violations by @lukekim in #9050
- Fix Docker build failing to copy shared libraries due to ldd output parsing by @phillipleblanc in #9058
- feat: Change /v1/sql and FlightSQL to use local execution in cluster mode by @phillipleblanc in #9055
- Remove unmaintained dependencies by @lukekim in #9045
- Enable cayenne + changes stream by @Jeadie in #9053
- feat(cli): add
spice querycommand for async queries REPL by @phillipleblanc in #9057 - Remove unncessary allocations by @lukekim in #9059
- Add
dataset_acceleration_size_bytesmetric by @krinart in #9062 - Fix tracing of
sql_querybeneathtool_use::sample_data. by @Jeadie in #9043 - Basic script to run distributed spice by @Jeadie in #9049
- Add integration tests for Acceleration Snapshots by @krinart in #9067
- Upgrade CUDA toolkit to 12.6.0 by @sgrebnov in #9079
- Install required protoc dependency for CUDA build by @sgrebnov in #9080
- feat(cluster): add executor control stream heartbeat by @phillipleblanc in #9072
- feat: Fix async queries API and integrate Ballista shuffle improvements by @lukekim in #9075
- Remove models variant (now default) & Windows builds (use WSL) by @lukekim in #9063
- Cayenne: share upload semaphore across partitions to bound memory growth and optimize I/O by @sgrebnov in #9078
- Snowflake data connector - add
snowflake_private_keyparameter by @ewgenius in #9085 - Rewrite Go CLI in Rust by @phillipleblanc in #9061
- GCS Data Connector (Alpha) by @lukekim in #9084
- Skip 'latest' Docker tag for pre-release versions by @sgrebnov in #9077
- Add HTTP endpoints for acceleration snapshots API by @phillipleblanc in #9065
- Cayenne: Allow append mode with both primary_key and time_column by @sgrebnov in #9090
- Add Cluster Observability (Metrics+Dashboard) by @phillipleblanc in #9066
- proto for 'CayenneAccelerationExec' by @Jeadie in #9094
- Add 'anthropic-beta' header for structured outputs by @Jeadie in #9093
- Cayenne: refactor write path to use insert_into() as single entry point (part 1) by @sgrebnov in #9088
- Fix testoperator dispatch by @sgrebnov in #9097
- Fix setup-spiced GH action (_models suffix does not exist anymore) by @sgrebnov in #9102
- build(deps): bump github/codeql-action from 4.31.10 to 4.31.11 by @app/dependabot in #9108
- Remove
DistributeFileScanOptimizerandUnionProjectionPushdownOptimizer& settarget_partitionsdynamically based on cluster capacity by @phillipleblanc in #9100 - build(deps): bump zip from 2.4.2 to 6.0.0 by @app/dependabot in #9111
- fix: Preserve query parameter order in HTTP connector to match filter values by @sgrebnov in #9114
- Add PollNow interrupt for Ballista executors to reduce task scheduling latency by @phillipleblanc in #9098
- Revert "GCS Data Connector (Alpha) " by @lukekim in #9084
- Fix stack overflow for CDC batching by @krinart in #9115
- fix: update Ballista fork to include executor timeout fix by @phillipleblanc in #9124
- Properly propagate SIGINT/SIGTERM from CLI to runtime by @krinart in #9127
- fix: Use the same vortex dependency as ballista by @peasee in #9123
- release: Bump version to 1.11.0 for stable - https://github.com/spiceai/spiceai/commit/14d09f8e262008df69ded898ed3bebee08471508/
- Cayenne snapshots with shared metadata by @lukekim in #9118
- Improve error handling for URL tables with Azure URLs by @phillipleblanc in #9129
- Add missing Windows build step for spice CLI in build_and_release workflow by @phillipleblanc in #9143
- Fix install-dev to use debug build path for spice binary by @phillipleblanc in #9142
- fix: CLI builds by @peasee in #9145
- Always create initial snapshots (unless bootstrapped) + when no snapshots exist by @krinart in #9119
- fix(cayenne): Fix upsert with pending deletions causing duplicate PKs by @sgrebnov in #9152
- fix(flightrepl): Add chrono-tz feature to flightrepl for timezone formatting by @sgrebnov in #9153
- fix(delta_lake): Preserve container name in ABFSS URLs for Azure Delta Lake tables by @sgrebnov in #9155
- fix: Make CLI system and asset type detection more robust by @peasee in #9148
- fix: Set query set properly on benchmarks telemetry metrics attributes by @peasee in #9162
- fix: Download _models variant - https://github.com/spiceai/spiceai/commit/27f3058d0007595b02c198755c3b22319032ff30/
- fix: Helm chart image tag - https://github.com/spiceai/spiceai/commit/7405c8df0db4ecce0ed6d4a4d424553d604b9036/
- Revert "Remove models variant (now default) & Windows builds (use WSL) " by @lukekim in #9063
- fix(cli): Several CLI fixes from the Go to Rust migration by @lukekim in #9157






